Overview
Tutorials are designed to offer a guide to complete common objectives, while also acknowledging that individual developers need to respond to individual needs of their own solutions. Tutorial frameworks provide blueprints for these solutions and should be adapted to fit individual needs.

Analytics with Birst
Infor’s end-to-end, enterprise-caliber analytics tool.

API Gateway
A comprehensive set of components to securely connect disparate systems across the enterprise ecosystem.

Application Development with Mongoose
Infor’s rapid application development framework that offers users a no-code/low-code/full-code experience.

Artificial Intelligence
Infor AI opens up the world of machine learning to a wider array of business users through its visual modeler, allowing for deployment of models with low-code and no-code implementations.

Analytics & Reporting in CloudSuite Service Industries
Infor’s CloudSuite Service Industries (CSSI) reporting and analytics platform offers a robust and comprehensive suite of tools and capabilities to help businesses manage, analyze, and visualize data.

Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Infor BaaS (Backend as a Service) enables you to build services locally and deploy them in a cloud environment.

Data Fabric
Infor’s comprehensive, cloud-native data management and processing platform.

Digital Assistant
Infor’s Digital Assistant is a virtual employee that any business can teach to answer questions and speed access to knowledge.

Document Management
Infor Document Management provides robust digital document storage, searching, printing, and integration capabilities.

Governance, Risk and Compliance
Infor GRC is a comprehensive approach to managing the risks, compliance, and governance of an organization.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Overview
Analytics with Birst
Infor Birst is an end-to-end, enterprise caliber analytics tool.
Birst delivers business intelligence and analytics dashboards to enable business decisions. Birst combines data from different sources in a single Networked BI platform. Reports, including charts, tables, geo maps, and key performance indicators, are organized into dashboards for presentation in a browser or a native mobile app. External content from other web pages can also enhance the end user experience.
Birst is available as a multi-tenant cloud architecture or as an Appliance for in-house deployments.
The Birst Networked BI platform combines the capability, scale, and data governance required for enterprise data with data from end users to create a blended data platform. Centralized and decentralized teams can leverage trusted corporate data along with local data for agile, robust business analytics.
The Birst Connectivity Framework provides access to data in the enterprise, whether it is in an existing data warehouse, in flat or structured files, or in cloud business applications. Birst extracts data from those sources, then organizes it and models it into a user data store, making the data ready for analysis. Birst does this using Automated Data Refinement (ADR) and a transformation language (ETL) to automatically merge data and create the data store, unlike the lengthy and complex work needed to create a traditional data warehouse. The data store unifies your data from multiple sources, refines it for business use, and provides a consistent view of all data to all users.
To augment the content in the user data store, Birst Live Access can directly query on-premise data sources in real time.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Automated Data Refinement (ADR) | Patented technology that automates the process of creating a robust dimensional model and semantic layer. |
Networked BI | Brings both centralized and decentralized data together to provide governed data in an agile environment. |
Semantic Layer | A business representation of complex company data for end user consumption. |
Orchestration | Provides a module to create and manage workflows for data extraction, processing, and space operations. |
Enterprise Space | Enable complex, scalable data management with dimension data models. |
Professional Space | Relational data model with low code, now code self-service data preparation. |
Birst Query Language (BQL) | A proprietary logical query language for defining expressions. |
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) | A process in database usage and especially in data warehousing that involves extracting data from outside sources, transforming it to fit operational needs, and loading it into the target database or user data store (warehouse). |
Component Parts
Birst provides an integrated Networked BI platform for data-driven analysis.
Birst includes:
Birst Home | The Birst Home page is your starting point. It shows the spaces, the containers that organize and hold data, metadata, reports and dashboards. An account may have one space or use separate spaces with different sets of data for different analytical purposes. Home is the entry point for BI developers, data analysts, and administrators to work with data in Birst. Business user accounts can be configured to directly open dashboards and bypass Home. |
Dashboards | Dashboard authors create and view interactive dashboards that contain reports built in Designer and Visualizer. Business users can browse the dashboards, drill down into details, and share them via email. In addition to viewing dashboards in web browsers, end users can access them from Birst Mobile apps. The new generation of Birst Dashboards is based on responsive design principles and promotes highly interactive user experiences. Organize Visualizer and Designer reports onto dashboards, add powerful filters, key performance indicators (KPIs), geo maps, and text boxes, and group dashboards into collections. |
Visualizer | Business users and report writers access Visualizer to explore enterprise data and quickly get answers to business questions. Visualizer helps business users and report writers to rapidly answer questions and discover information. You don’t have to have formal expertise to interact with the drop-down menus and drag-and-drop columns. You can save and add reports to dashboards. |
Designer | Designer is a tool for Data analysts and report writers. It provides pixel-perfect layout capabilities and advanced functionality such as column selectors and drilling. Use Designer to develop highly formatted enterprise reports that you want to print, schedule for email delivery, or export. |
Admin | Developers, data analysts, and administrators use the Admin interface to create and manage the user data store, report catalogs, user accounts, and access permissions. The Admin module provides both data and system-related operations. Access to functionality is based on your user permissions. Data processed in Admin is available for analysis and reporting in Designer and Visualizer. |
Connectivity Network | Birst provides various ways of connecting to your existing data: Birst Connect is a Java Web Start application that automates uploading and processing data in Birst. It runs behind your firewall in order to access files and data sources at your location. Birst Connect uses HTTPS and supports JDBC data sources and SAP. Birst Live Access allows Birst to access data resident in local data marts and data warehouses without requiring that data to first be uploaded into Birst. Application Connectors provide access to many enterprise applications including Marketo and Salesforce. Upload Filessuch as Microsoft Excel, Access, or delimited ASCII text. |
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out the Analytics Cheat Sheet.
Topical Videos
Need information on a specific feature or function or a quick overview? These short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our Infor Analytics playlist on YouTube.
Written Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see Infor Birst documentation.
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in the Infor Birst Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Analytics with Birst
API Gateway
Overview
The ION API Gateway is a NodeJS reverse proxy application. In the simplest terms, ION API gateway accepts incoming HTTP requests from clients (web-apps, mobile-app, fat-clients, etc.), passes the request on to the proper target server, and returns the target server’s response back to the client.
In addition to simply passing requests and responses through, the ION API can add value for adjusting or enriching the request and response via the use of policies. Policies can, for example, add headers to the request or log values from the response.
The following features describe the API Gateway
- Pass-through (Proxy)
- Orchestration
- Hybrid
- Backend as a service (BaaS)
Key Concepts & Definitions
ION | Intelligent Open Network. Part of the Infor OS technology platform. |
BOD | Business Object Document. An XML document based on standards from the Open Application Group Integration Specification (OAGIS). |
ION Desk | A business representation of complex company data for end user consumption. |
Monitors | A monitor verifies incoming documents against a monitoring rule. If the result of this evaluation is true, the monitor generates an alert. The alert is sent to the users that are based on a distribution list. |
Workflows | Workflows enable communication from an application to a user. For example, it presents a document for approval or prompts the user to perform a task using a particular screen of an application. |
Activation Policy | A workflow activation policy contains a monitoring rule that evaluates incoming Sync BODs, and a mapping feature to map BOD attributes to workflow parameters. |
Workflow Schedules | A workflow schedule is an automatic way to start workflow instances at regular intervals of time. A schedule is a sequence of “runs”: each time the schedule timer issues a trigger, the workflow schedule attempts to start a workflow instance. Depending on the schedule configuration, a new workflow instance may be started for each “run”. |
Business Rules | Approval matrices contain rules, that are based on parameter evaluation, for distribution of approval tasks. These matrices can be used from Workflow to define approval chains |
Want to learn more?
Written Guides
Product documentation serves as the primary reference for understanding specific product functionalities. For online, searchable, and user-friendly resources, refer to the following documentation.
Quick Reference
Download the API Gateway Cheat Sheet
Community
Collaborating with peers in your sector offers a valuable opportunity to learn and assist others. Dive into the Infor OS Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor- led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- API Gateway
Application Development with Mongoose
Go beyond basic fit and customize your cloud experience with extensibility tools that leverage no-code, low-code, and full-code frameworks.
Infor Mongoose is Infor’s rapid application development framework. It offers users a no-code, low-code, or full-code experience. This means our framework can benefit our customers regardless of their technical expertise.
Whether you are building an extension to one of our Infor ERP’s or building a complete stand-alone application, Mongoose will help you design, build, and deploy quickly and easily. Mongoose maximizes a developer’s time by utilizing various wizards to reduce the need to “drop into code” and by exploiting our flex layout, user components and HTML5 designer, you will be confident that Mongoose will provide you with the ability to create the UX/UI your company is looking to achieve.
The framework also comes with many built in features like, a full reporting engine, integrated workflow, full user management, and a robust background task manager. All things that most applications could need to leverage right at your fingertips.
Concepts & Definitions
Development Framework | A software framework that provides a standard structure and set of components to help developers build applications. |
Extensibility | The ability of a software system to be extended with new features or functionality without major changes to the existing code. |
Low Code | A development platform that provides a visual environment for building applications with little or no coding with the use of a library of pre-built components that can be assembled with drag-and drop. |
Full Code | The ability to include Custom Assemblies and form scripting to your application. |
Metadata | Data that translates and connects the backend data to the front end data. |
Runtime Mode | Mode in which users can use and interact with the application in normal day-to-day operations. |
Design Mode | Mode in which developers can edit and modify forms in the application. |
Components
Forms | A window through which you can interact with information in a database. |
Fields | An area within a record which is reserved for a specific piece of data. |
Records | A collection of values or fields of related information. |
Collections (IDOs) | An IDO (Intelligent Data Object) collection consists of a set of properties that make up a collection of information that can be API or table based. |
IDO Extension Class | a .NET class that allows developers to extend the functionality of an existing IDO by adding methods and event handlers. IDO extension classes are compiled into a .NET class library assembly and stored in the IDO metadata database. |
Application Event System | The application event system is a powerful and flexible set of tools that is designed to help extend and customize how the system works. You can use these tools to define and monitor application events across the system, rather than being limited to a single form. |
DataViews | Advanced data grids that you can create to query a custom set of data, quickly and easily. The basic DataView presentation is similar to an Excel spreadsheet, displaying data in columns. |
Critical Numbers | Key performance indicators, or KPIs, that you can use to get a quick view of important statistics or track progress. |
Runtime Builder | Tool used for a specialized set of Mongoose forms that are designed to allow authorized users to create simple forms in Runtime Mode, without having to enter into design mode. |
FormSync | Utility that can be used to retain and upgrade customizations made in the previous version of the application. It can also be used to copy customized objects from one forms database to another. |
Form Control | Form Control is a version-control tool for objects being developed for the presentation layer (client tier) of an application in Windows client. |
Key Benefits & Integrations
- Rapid Application Development
- Easy and powerful integration to ERPs
- Automatic Web Deployment and Multi-Device
- ION Enabled core toolset
- Cloud enabled for both dev and deployment
- Personalize applications, upgrade automatically
- Simple and flexible installation
- Full ION Integration
- Interfaces with JSON
- API Gateway Integration
- Restful Web Services
- DataLake/IoT
- Outrigger Connections
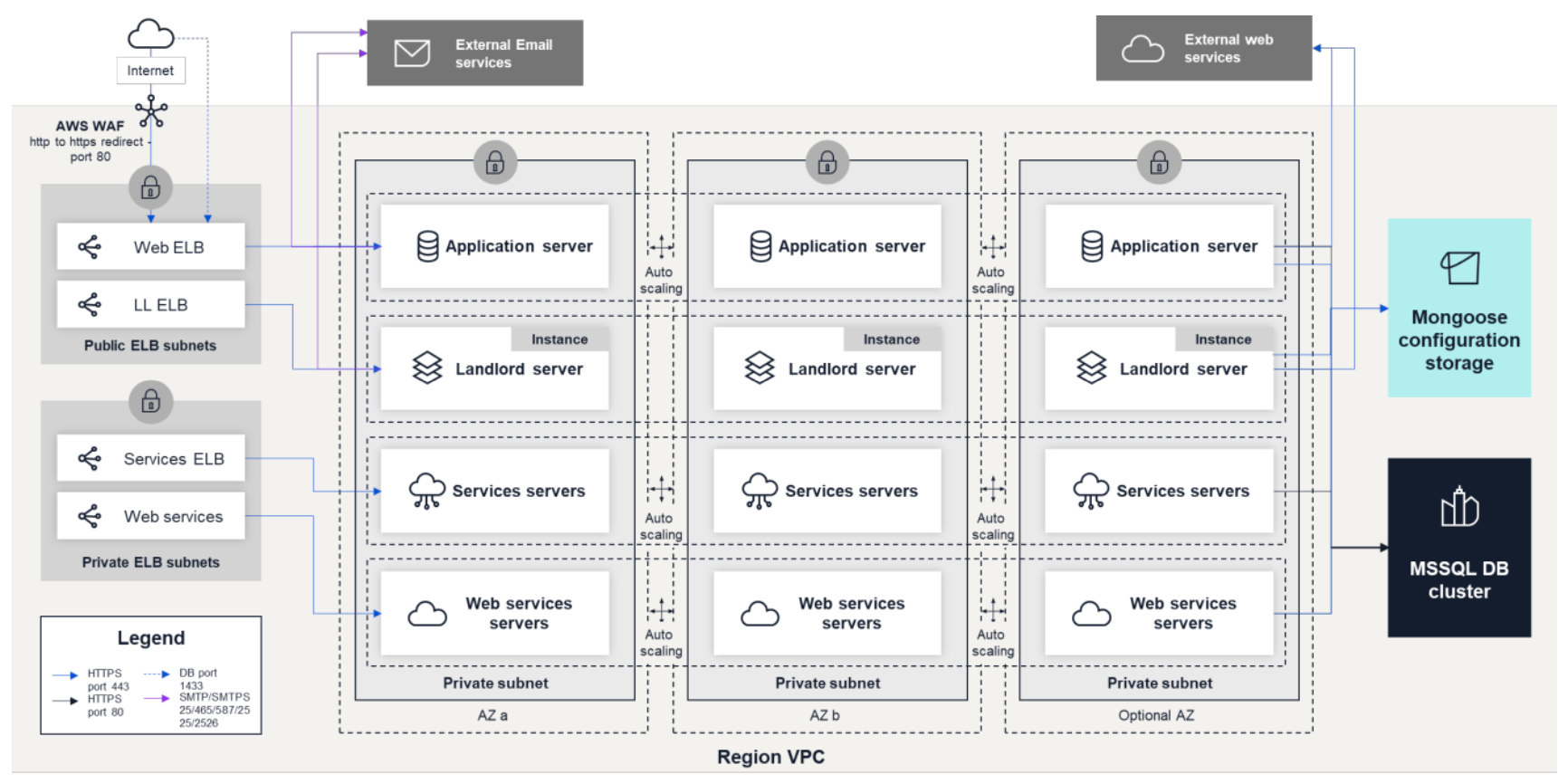
Architecture
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There are numerous valuable resources available to enhance your understanding of the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is one of the most helpful tools, which can provide a concise overview of key information. You may find the following Cheat Sheet particularly useful for your learning and reference purposes.
Courses
Infor U Campus offers learning tracks that combine video-based and instructor-led teaching. If you are an Infor customer, check out the Mongoose courses available on Infor U.
Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature, function or just a quick overview? These short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Written Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see this component’s documentation.
On this page
- Application Development with Mongoose
Artificial Intelligence
Use Machine Learning to build an AI into your business processes.
Machine Learning (ML) is a category of Artificial Intelligence (AI), computer science, and mathematics that focuses on using data and algorithms to train models and use those models to make predictions on new and unseen data. Infor AI opens up the world of machine learning to a wider array of business users through its visual modeler, allowing for deployment of models with low-code and no-code implementations.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Infor AI | Infor’s machine learning platform, a component of Infor OS. |
Quest | A flow of activities that make up the machine learning model. |
Training Quest | A quest involving a predictive method that produces a trained model. |
Trained Model | A model that can be used to predict outcomes based on new data. |
Production Quest | A trained model that has taken steps to deployment. |
Endpoint | The REST API access point of a real time production quest to process new data through the model. Endpoints can process data by being passed a CSV, a JSON message, or accessed via the API gateway. |
Data Lake | Flexible and economical cloud object storage solution where data is stored in its raw format. This is Infor AI’s primary data source. |
Label/Target | Terms that refer to the prediction of the model. |
Categorical | Data types that are non-numeric in nature and belong to a category instead. E.g. “Country of Residence”. |
Supervised Learning | Machine learning algorithms that form relationships between targeted label and input features so that the output values for unseen data can be predicted. Supervised algorithms must be trained on known outcomes. |
Unsupervised Learning | Machine learning algorithms that make inferences from data using only input features without referring to known or labelled outcomes. These algorithms can discover data structures by clustering it into intuitive groups. |
Best Practices
A machine learning project has a lot of flexibility and user control over it, but it is generally accepted that an ML workflow adopt the product life cycle below.
Business Case Definition
Before starting a machine learning project, it is best to step back and define the business problem at hand. It takes some finesse to match business problems with the appropriate algorithms, and the appropriate data. Often, business problems fall into one of the following categories.
Fetching Data
The enterprise can produce incredible amounts of data from different systems. For use in the Infor AI platform, data should be managed and stored in the data lake.
Data Preparation
Data preparation tasks can be numerous and time consuming. It is recommended that one be familiar with tidy data standards when it comes to cleaning data. It is also important to understand any caveats to the particular algorithm that you might use to process the data. Infor AI has the following built in tools for data manipulation and preparation, as well as the ability to run python scripts to allow for complete customization when manipulating data.
Select Columns | Select or exclude a subset of columns from the current dataset. |
Remove Duplicates | Remove duplicates in selected features. |
Construct Feature | Create a new feature out of the existing ones by using mathematical, logical, or casting operations. |
Index Data | Transform categorical values into numeric for the selected columns. Each category will be assigned a number according to its occurrence in the data, highest occurrence having number 0. |
Smooth Data | Remove noise from a dataset to allow natural patterns to stand out. |
Split Data | Split the dataset into training data and test data by specifying the split ratio for the training dataset. |
Scripting | Execute a customized Python script to perform an activity which is not available in the catalog. |
Ingest to Data Lake | Ingest data to Infor Data Lake |
One Hot Encoder | Transform categorical features into a binary matrix (vectors) to distinguish each categorical label. The vector consists of 0s in all cells, with the exception of a single 1 in a cell used uniquely to identify the label. |
Feature Scaling | Scale features with varying magnitudes, units and range into normalized values. |
Handle Missing Data | Replace missing values in selected features (with mean / mode / constant value / interpolation), or remove the entire row exceeding a selected ratio of missing data. |
Target Encoder | Numerization of categorical variables via target – replaces the categorical variable with just one new numerical variable and replaces each category of the categorical variable with its corresponding probability of the target (if categorical) or average of the target (if numerical) |
Edit Metadata | Select the Target label. Edit the metadata of the selected features by changing its data type, tagging the categorical values, changing the variable name or defining their machine learning type. |
Balance Data | Balance the dataset using undersampling or oversampling methods. |
Execute SQL | SQL operations (filter out data, join datasets, aggregate data etc.). |
Model Training
Training a model requires the prepared dataset and the algorithm to be used in training. Supervised algorithms can be scored for accuracy using the train/test split functionality and the score and evaluate model blocks. The compare model block will allow for the training of multiple models to compare performance statistics.
Model Fitting & Tuning
Algorithm hyperparameters are available in each of the algorithm blocks. The specific parameters will be different depending on algorithm selection, and can details for each hyperparameter can be found in the documentation of the chosen algorithm.
Model Deployment
In the quest, select the checkbox on activities desired for the deployed model and push the activities to the production quest. This quest can be deployed as an endpoint accessible via the ION API gateway.
Model Maintenance
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out this Cheat Sheet.
Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature or function? Or how about a quick overview? Then short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Product Documentation
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see this component’s Documentation.
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in this component’s online Community.
On this page
- Artificial Intelligence
Analytics & Reporting in CloudSuite Service Industries
Infor’s CloudSuite Service Industries (CSSI) reporting and analytics platform offers a robust and comprehensive suite of tools and capabilities designed to help businesses manage, analyze, and visualize their data. Customers using CSSI applications typically require a variety of reports to manage and analyze their business processes effectively. Common types of reports delivered and supported include:
- Operational Reports
- Configurable Ad-hoc Reports
- Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) Financial Reporting
- Analytics Platform for CloudSuites (CloudSuite Analytics)
- Birst Enterprise
- API Support
- SQL Support
Key Concepts and Definitions
Operational Reports | Focuses on the day-to-day operations of an organization. Provides real-time information about the current state of business processes. Uses Infor delivered reports or create custom reports. |
Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) | Financial planning, budgeting, and forecasting. Financial consolidation reports. Capital expenses planning. |
Configurable Ad-Hoc Reports | Create reports on the fly. Microsoft Excel integrations allow you to download cloud data to the desktop, or upload from the desktop to the cloud server. Easy to use – no IT programming resources needed. |
Infor Analytics Platform for CloudSuites (CloudSuite Analytics) | End-to-end, enterprise-caliber analytics tool. Automatically delivered with your applications – no additional license required. Delivers industry-specific business intelligence and role-based analytics content to enable business decisions. Delivers ETL data models designed by core application data experts. Inherits application security policies. Delivers pre-built content including: Dashboards. Charts. Tables. Geo maps. KPIs – key performance indicators. Support for presentation in a browser or mobile app. |
Birst Technology (Birst Enterprise) | The technology layer that hosts CloudSuite Analytics. Upgrade option – requires an additional license. |
Automated Data Refinement (ADR) | Patented technology that automates the process of creating a robust dimensional model and semantic layer. |
Networked BI | Patented technology that brings both centralized and decentralized data together to provide governed data in an agile environment. |
Semantic Layer | A business representation of complex company data for end-user consumption. |
Orchestration | Provides a module to create and manage workflows for data extraction, processing, and space operations. |
Enterprise Space | Enable complex, scalable data management with dimension data models. |
Professional Space | Relational data model with low code, no-code self-service data preparation. |
Birst Query Language (BQL) | A proprietary logical query language for defining expressions. |
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) | A process in database usage, especially in data warehousing, that involves extracting data from outside sources, transforming it to fit operational needs, and loading it into the target database or user-data store (warehouse). |
Operational Reports
Operational reporting focuses on the day-to-day operations of an organization. It provides real-time or near-real-time information about the current state of business processes.
Operational reports provide powerful and immediate access to live transactional data, provide timely reporting responses to daily operational questions, and provide the global business community with the ability to manage daily tasks efficiently, ensuring smooth business operations.
Features and Tools
- Real-Time Data: Provides up-to-the-minute data for immediate decision-making.
- Detailed Transactional Data: Focuses on specific transactions, such as sales orders, purchase orders, staffing, inventory levels, etc.
- Operational Dashboards and Alerts: Includes dashboards and alerts to monitor real-time business transactions, one-click access to exception reporting, drill down and drill across access to related reports, and up-to-the-moment critical metrics you need to make on-the-spot business decisions.
- Infor Delivered Reports: Delivers Out-of-the-box (OOTB) operational reports that meet industry standard reporting and compliance requirements for daily business processing.
- Application-Specific Reporting: Delivers OOTB reporting specific to your business’ daily processing from various applications, including finance, HR, workforce management, supply chain, and manufacturing.
- Quick data export: Export data to Excel and PDF formats, getting data down from the cloud to your local environment. Many applications also support uploads from Excel to the cloud database.
- Delivered Security Models: Configurable OOTB security models to enforce data protection, confidentiality, integrity, compliance, internal controls, and trust.
- Audit Reporting: Standardized audit reports to ensure regulatory compliance, financial transparency and accuracy, and corporate governance.
- Report Catalog: Access all delivered and configured reports in the system, filter by application, and favorite the reports you access most often.
Use Cases
- Daily Sales Reports: Monitoring daily sales performance.
- Inventory Management: Checking current inventory status to manage stock effectively.
- Order Tracking: Tracking the status of customer orders in real-time.
- Production Monitoring: Monitoring production processes to ensure they are running smoothly.
- Financial and Payables Processing: Real-time visibility into cash flow, invoice payments, vendor activity, and financial data.
Configurable Ad-Hoc Reports
Many reporting needs can be met using Infor-delivered reports. However, many organizations need configurable ad hoc reporting tools to meet their unique reporting requirements.
Infor provides several report development tools and platforms that allow your business to create configured reports tailored to your specific business needs. Reporting development tools range from quick and easy to complex to meet the needs of your custom reporting requirements and the skill sets of your employees.
Features and Tools:
- Excel Integration: Create ad-hoc Excel reports that don’t require extensive technical knowledge or assistance from the IT department.
- Configurable Reports: Convert data on a screen to a report that can be configured. Add or remove fields, change labels, schedule reports, and share reports with your colleagues.
- Copy or Create Analytic Reports: Copy and modify delivered analytic reports, visualizations, or dashboards. Create simple or complex analytic reports from scratch using the Birst technology platform.
- Advanced Reporting Tools: Extract data from the Infor Data Lake using a variety of tools including SQL-based Compass queries, Compass query APIs, Data Lake APIs, and Compass JDBC Drivers.
Enterprise Performance Management
Gain a complete, real-time view of your financial business performance with Infor Enterprise Performance Management (EPM).
Many organizations still perform budgeting and planning in error-prone spreadsheet silos that consume a significant amount of time, money, and resources on highly manual processes. Modern EPM software can help reduce errors and enable enterprise-wide collaboration with an integrated, closed-loop approach.
Infor Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) is a modern, mobile-enabled financial performance management and business intelligence platform that provides a complete range of integrated enterprise performance management capabilities that let you report with confidence.
Infor EPM can be tightly integrated into an organization’s enterprise data sources via the Infor OS data fabric; it can also leverage additional advanced industry analytics capabilities with CloudSuite Analytics powered by Birst®.
Features and Tools:
- Financial planning, budgeting, and forecasting: Create budgets and plans, forecasts, and operational and strategic plans.
- Financial Consolidation Reports: Standardized reporting tools for Income Statements, Assets, Liabilities, P&L, Cash Flow, Budgeting & Planning, account analysis, and audit trails.
- Capital expenses planning: Manage capital with documentation packages, an overview of statuses, and approval.
Additional Resources for EPM Reporting:
Enterprise Performance Management | EPM software | Infor
CloudSuite Analytics
CloudSuite Analytics delivers industry-specific role-based business intelligence that provides business insight into past, present, and future trends. Driven by Birst technology, these pre-built insights enable your teams to make intelligent business decisions.
Delivered pre-built content includes the following:
- Application data model
- Dashboards
- Charts
- Tables
- Geo maps
- KPIs – key performance indicators
Within CloudSuite Analytics, customers can change any report, dashboards, KPIs, metrics, subject areas, metadata, orchestration & pre-built data model (add fields from CloudSuite – user defined fields).
Infor does not recommend changing content delivered by Infor. Instead, it’s recommended to copy the object and make updates to the copied object. This will prevent potential disruption when content updates are applied.
**CloudSuite Analytics does not allow for importing data from different sources.
**CloudSuite Analytics is only available in the Multi-tenant cloud and is not supported for on-premise deployments.
Inventory Manager Dashboard
Birst Enterprise
Birst Enterprise is an upgrade option available as a multi-tenant cloud architecture. Customers who purchase the Birst Enterprise upgrade option can use all the standard CloudSuite Analytics features and the following additional capabilities:
- Connect to additional Infor and 3rd party data sources, combining data into a single source-of-truth BI solution.
- Add users outside of Cloudsuite.
- Connect to external content from other web pages to enhance the end-user experience.
The Birst Networked BI platform combines the capability, scale, and data governance required for enterprise data with data from end users to create a blended data platform.
The Birst Connectivity Framework provides access to data in the enterprise, whether in an existing data warehouse, in flat or structured files, or in cloud business applications.
Birst extracts data from those sources then organizes it and models it into a user data store, making the data ready for analysis. Birst does this using Automated Data Refinement (ADR) and a transformation language (ETL) to merge data, create scripts, and publish to the data store. The data store unifies your data from multiple sources, refines it for business use, and provides a consistent view of all data to all users. The data store is used to create and configure your own reports, visualizations, and dashboards.
API Support
Infor’s reporting and analytics platform provides advanced API support for operational transactional data and replicated data in the Data Lake. APIs can also be used for data integrations between systems.
Click here for Infor API documentation.
SQL Support
Data Lake Compass query functionality provides robust query capabilities to search and extract results from data stored in Data Lake.
Query functionality is available through the Compass UI in Data Fabric, the Infor OS Compass API endpoint, and the Compass JDBC driver.
Want to learn more?
There are several reporting and analytics tools to choose from.
Reference Guides
For Birst technical reference, check out the Analytics Cheat Sheet.
Topical Videos
Need information on a specific feature or function or a quick overview? These short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our Infor Analytics playlist on YouTube.
Product Documentation
Documentation for all Infor products, including reports and analytics, is available on Infor’s documentation website. Click here to access Infor’s Documentation Website.
Infor Community
Interested in collaborating with others in your industry? Joining a community is a great way to learn and help others. There are several to choose from! Here’s a few that can get you started, and there are many more to choose from. Join the Infor Birst Community Join the FSM (CSF) & HR Talent (HCM) Community Join the M3 Customer & Partner Community
Infor U Courses
Infor U offers prescriptive industry-specific learning paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Analytics & Reporting in CloudSuite Service Industries
Analytics & Reporting in M3 Cloudsuites
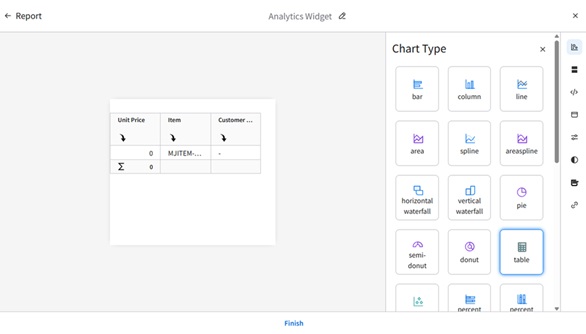
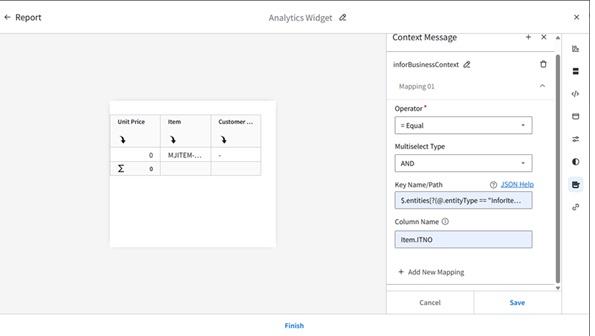
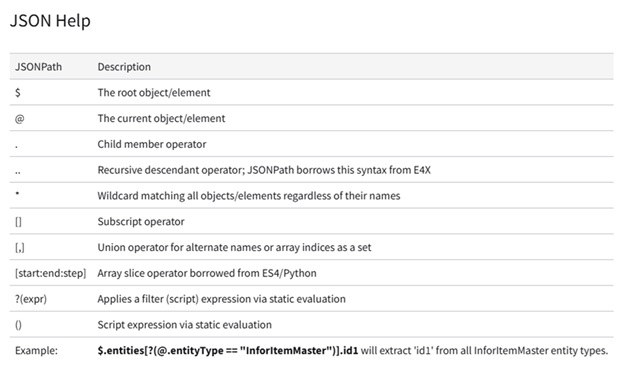
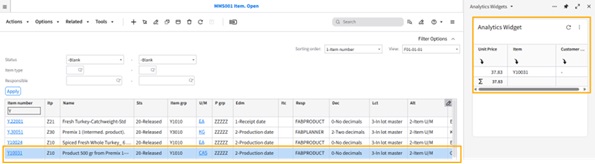
Configuring Context Message in the Visual Analytics Widget
Beginner | 10 Minutes
Overview
This Tutorial provides instructions for setting up an analytics widget with a context message in the Infor OS Portal. For our example, we will track the lowest price of an item within the last 30 days by directly selecting the item number in M3.
📋 Requirements
|
Tutorial
A video walk-through of the tutorial is available below.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Analytics & Reporting in M3 Cloudsuites
Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Overview
If you want to create a new API that invokes other APIs through a programming language, BAAS is the right choice. With BAAS, you can choose between Java or Typescript languages, create your project in Visual Studio Code using the BAAS extension, and deploy the project in your tenant, which creates a new API for you in the API suite
Want to learn more?
Written Guides
Product documentation serves as the primary reference for understanding specific product functionalities. For online, searchable, and user-friendly resources, refer to the following documentation.
Quick Reference
Download the Backend as a Service Cheat Sheet
YouTube
Check out our Backend as a Service Playlist on YouTube.
Community
Collaborating with peers in your sector offers a valuable opportunity to learn and assist others. Dive into the Infor OS Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Data Fabric
Manage data on the platform so that humans and systems can securely access information from anywhere.
Infor Data Fabric is Infor’s comprehensive, cloud-native data management and processing platform. Data Fabric features spanning big data storage and query interfaces, real-time data delivery, and a suite of advanced data management tooling to structure the big data generated by Infor’s CloudSuite applications as well as third-party systems and data producers.
Infor Data Fabric centralizes common enterprise data requirements, development patterns, and tooling into a unified suite of tools to maximize data ROI that scales with continued data growth and capture.
At the center of Data Fabric is Infor’s Data Lake which uses an object storage architecture to provide long-term persistence of data in its raw, original format. CloudSuite applications and 3rd party applications, tools, and services can replicate transactional and master data for eventual processing and query analysis.
Data movement into and out of the Infor Data Lake is facilitated with a suite of tools and interfaces that include event-driven workflows orchestrated through Infor’s iPaaS platform, API endpoints, JDBC driver, and user-friendly UI interfaces. The Infor Data Fabric application also includes interfaces and tools for data query, exploration, data quality management, data cataloging, business domain metadata management, and development infrastructure.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Data Fabric | Infor’s comprehensive, cloud-native data management and processing platform. |
Data Lake | Infor’s central big data storage repository leveraging object storage architecture to provide long-term persistence of data in its raw, original format. |
Data Object | Data Lake data is stored as data objects. Data objects are formed from the sent raw data and the data object properties. |
Atlas | Data Object Explorer UI experience for viewing and managing data lake objects. |
Compass | A suite of tools that provide data consumers with interfaces for connecting to and processing ANSI SQL queries against data objects stored within the Data Lake. Supported object formats: NDJSON & DSV (CSV, TSV, PSV, or user-defined). |
Data Lake Flow | A sequence of activities orchestrated by ION that results in sending and/or retrieving Data Lake data. |
Data Catalog | The Data Catalog stores metadata about data objects that are used within the organization. |
Data Loader | An application that facilitates the one-time loading of multiple database tables at once directly to Data Lake. |
Metadata Crawler | A wizard that facilitates generating object metadata for tables, views, and materialized views stored in a database. |
Data Egress | The outbound transmission of data that traverses Infor’s cloud boundary on request of a user, client, application or system. |
Data Ledger | Reconciliation tool that aids data administrators in identifying alignments or potential disparities between applications sending data to Data Lake and the Data Lake itself. |
Metagraph | Free-form modeling canvas and tool, used to define domain-specific resource models. |
Components
Application | The Data Fabric application allows you to view, manage, and query your data objects that are stored in Data Lake The Data Fabric menu includes these menu options: – Data Lake (Atlas, Compass, Data Ledger, and Purge) – Metagraphs – Utilities |
API Suite | RESTful APIs for: – Ingesting data into Data Lake – Retrieving data from Data Lake or querying Data Lake – Managing data objects |
Homepage widgets | – Data Lake Ingestion by object – Data Lake Ingestion over time – Data Lake Storage Overview (see also: Usage reports) – Atlas Upload |
Compass JDBC driver | The Compass JDBC driver can be used to query Data Lake data through a local SQL query tool. |
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out the Data Fabric Cheat Sheet.

Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature, function just a quick overview? Then short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Product Documentation
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see this component’s documentation
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in the online community today!
Courses
Infor Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video based and instructor led teaching. If you are an Infor customer then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Data Fabric
Digital Assistant
Streamline the user experience with a digital assistant that helps your employees navigate and access information by voice or chat.
Coleman Digital Assistant (DA) is the Natural Language Processing (NLP) based chat agent of Infor Cloud and third-party applications.
It works based on “Skills”, which represent a given ability to get essential information, perform a business task or navigate to specific screen. You can invoke a skill either by chatting or speaking with Coleman from a variety of interfaces, like Infor OS Portal, MS teams, mobile application.
A single skill consists of utterances, prompts, and responses. Utterances are your questions to Coleman. Prompts and responses are provided by Coleman in response to your utterances.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Before diving into building your own skills, the following table provides you with Coleman DA key concepts for better understanding each component of a Coleman skill.
Coleman DA | Natural Language Processing (NLP) based chat agent of Infor Cloud and third-party applications. |
Skill | A question or a series of questions that define the interaction between Coleman and the user to perform a business task. |
Intent | Represents an action that a user would like to perform using chatbot. |
Utterance | The phrase(s) provided by the user to invoke a particular skill. |
Slot/Requirement | User input variable(s) required to fulfill the skill. Can also be represented as a dynamic variable, which changes with every skill invocation. |
Fulfillment | Determines how your skill is executed and the end results are accomplished. |
Skill Chaining | Invocation of a second related skill after the first skill is completed. You can pass values from the first skill to the second skill. |
API Endpoint | API Endpoints deployed on API Gateway are used by Coleman DA skills as a means to communicate with the application either to perform a transaction or get specific information. |
API Flow | A composite API build by chaining many APIs which can be used in an API Fulfilment. |
Basic Skill | Basic skills are used to create the FAQ interaction. Those skills don’t require any back-end communication with other applications, which means that the fulfillment won’t call any API. |
API Based Skill | Advanced skills are used when Coleman-User interaction requires the communication with a particular application. In order to communicate with an application, Coleman will use the API endpoint deployed on API Gateway either to get application specific information or perform a transaction. |
Drill-Back Skill | Drill-back skills can take you to a particular screen either within the Infor OS portal using the drill back links or navigate to a particular website just by defining its address within a skill. |
Coleman DA Channels | |
Infor OS Portal | The Coleman chat window is part of the Infor OS Portal that can be access in context of any application within the portal. It has both the text chat and voice interaction feature. |
Infor Go | Coleman DA chat agent is accessible from the mobile application, Infor Go. It supports both text chat or voice interaction. |
Microsoft Teams | The Coleman DA application can be download and installed to have a conversation in your Teams application like you would with a live user. You can converse with Coleman though MS Teams in context of a particular tenant. |
API | Coleman DA exposes a set of APIs which can be used to interact with Coleman programmatically. |
Infor OS Portal | The Coleman chat window is part of the Infor OS Portal that can be access in context of any application within the portal. It has both the text chat and voice interaction feature. |
Infor Go | Coleman DA chat agent is accessible from the mobile application, Infor Go. It supports both text chat or voice interaction. |
Microsoft Teams | The Coleman DA application can be download and installed to have a conversation in your Teams application like you would with a live user. You can converse with Coleman though MS Teams in context of a particular tenant. |
API | Coleman DA exposes a set of APIs which can be used to interact with Coleman programmatically. |
Skill Flow Example
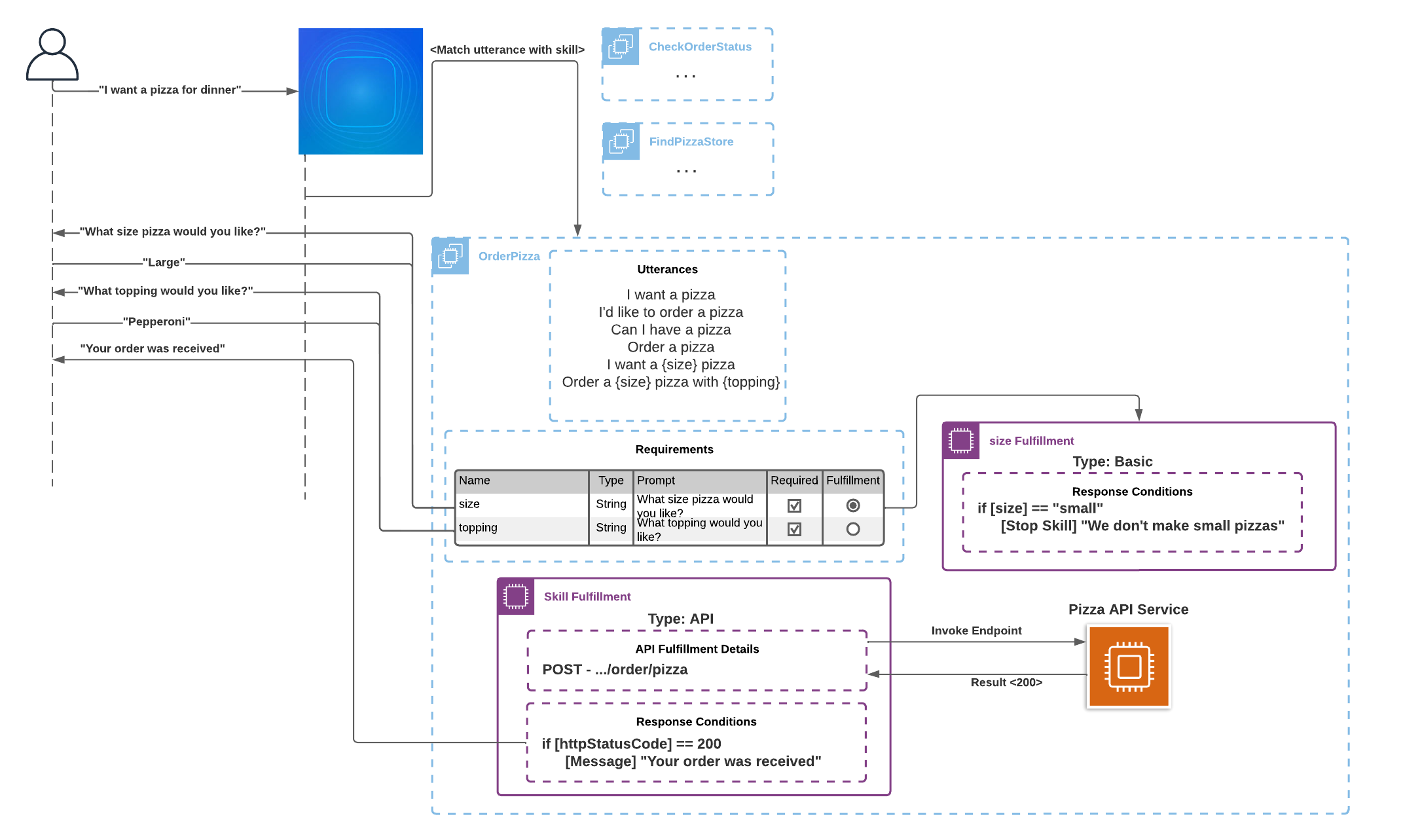

The diagram demonstrates the standard Coleman conversation flow from User skill invocation to Coleman’s final response. For better understanding of each component in the flow review the Table “
Best Practices
The table below presents the set of skill building ‘best-practices’ which helps in defining a high quality skills with desired UX:
Prompts | – For high-impact requests, consider a Confirmation Prompt before executing the Skill Fulfillment. – Define multiple prompts to help clarify whenever the user provides an invalid input. – Make sure all your requirement prompts are contextual for the user to know what Coleman is asking for. |
Requirements | – Define up to 3 requirements. – Give an example of the certain format expected in the requirement prompt. – Limit the usage of string or alphanumeric requirement types. – Use the Multiple Choice or Restricted custom requirement type if the expected prompt is a set of static values. |
Responses | – Do not respond with raw API payload details unless they provide sufficient information. – Include multiple responses for handling different types of errors. This can help the user understand the reason for the error. – Handle error gracefully. – Ensure there aren’t any holes in your conditions. – Ensure your response contains enough information to be useful. |
Security | – In case your skill requires restriction to a specific set of users/IFS security roles, define it on the skill level. |
Skill Basics | – Define a clear intent for your skill. – Any user-facing text should be grammatically correct. – The language used in your text should sound polite. |
Utterances | – In an utterance, do not include the word Coleman or reserved words such as: Help, Cancel, or Stop. – Consider unexpected ways a user might ask for a skill. – Have a variety of utterances to account for different invocation verbiage. – Consider regional dialects. For example, depending on where your user is located, paid time off may be referred as PTO, Vacation, Holiday, or Leave. – Use product or industry-specific lingo or acronyms. |
Want to learn more?
Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature, function or a quick overview? These short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Product Documentation
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see the:
Coleman Digital Assistant User Guide
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in this component’s User Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Digital Assistant
Document Management
Leverage Infor's central document repository to manage your enterprise document in the cloud.
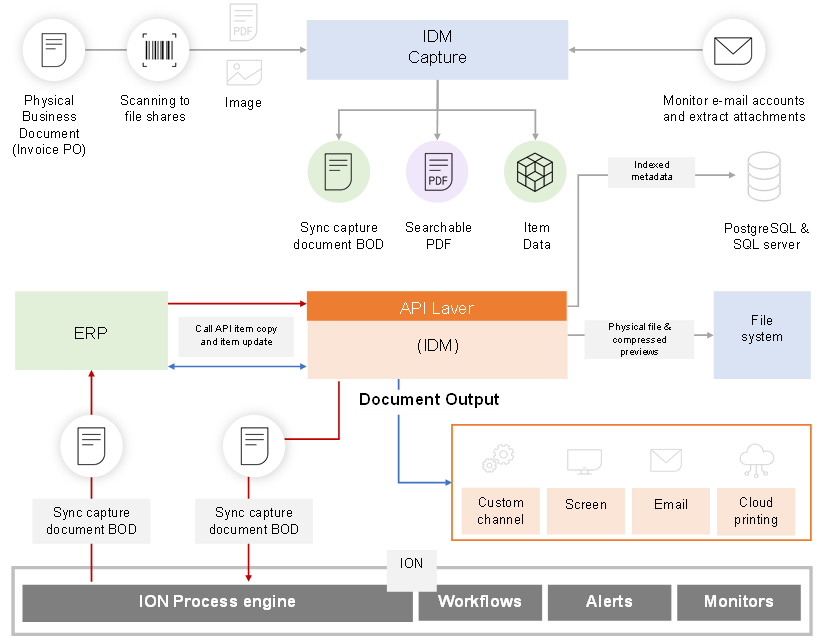
Infor Document Management (IDM) is a digital cloud-based document repository offered by Infor that delivers extensibility and business process integration throughout Infor OS. IDM offers comprehensive lifecycle management of documents including archiving, security, collaboration, and versioning.
IDM has the capability to scale vertically, horizontally, and globally, making it possible to manage millions of documents. Documents can be stored either locally on a database server or in the cloud. Furthermore, IDM’s Related Information contextual app provides context-aware information to Infor products, presenting IDM documents that are related to the selected asset.
IDM Capture streamlines the process of extracting, separating, and classifying important content by facilitating the automatic uploading of documents. Additionally, Document Output enables users to easily create templates, distribute emails, and print using Infor’s new Enterprise Print.
Key Concepts & Definitions
IDM | Shorthand for Infor Document Management IDM is a full-fledged document management system within Infor OS that can manage the entire document lifecycle of business documents, including creation , versioning, storage, retrieval, distribution, archiving, and purging. |
Document Output Management | IDM’s ability to create templates for document creation, the distribution of documents through email, and the ability to cloud print with IDM’s Enterprise Print feature. |
Output Management Templates | The capability to combine application data with customized templates to produce business documents. Templates can be created or modified using the Microsoft word add-in included with IDM. |
Contextual Applications | The related information contextual application provides the ability to display relevant documents stored within IDM alongside their corresponding business records. This is not limited to read-only access. Users can download, print, email, sign, or upload documents to IDM via the related information contextual application. |
IDM Capture | An optional add-on component, IDM capture provides optical character recognition (OCR) to transform unstructured content into meaningful data. Typically used for automating the AP invoice process but must be certified with the ERP. |
Document Type | An envelope for a document file and its metadata/attributes. Users can create any custom document type with any attributes needed such as height, weight, approval status, color. Flexible enough to cover all possible customer needs, a document cannot exist outside of a document type. Some applications provide default document types mapped specifically to their application record types. |
Attributes | Defined by the creator of a document type to store a characteristic. Can be used to create a reference between a document in IDM and a record in an Infor application. Can store: metadata, values, properties. Ex: item ID, supplier number, invoice number, purchase order number |
ACL | Shorthand for access control list. Consists of users, user groups, and privileges associated with each. These are applied to document types, permitting and restricting users’ actions on them. By default there are 2 types of ACL, public and private. Public is visible to everyone, private only to the last modifier of that document. Custom ACLs can also be created. |
Infor ION | Infor ION is an enterprise messaging system that integrates Infor products with each other and with non-Infor products. Transactional and master data is passed between products as business object documents (BODs) that are routed through Infor ION. Infor ION also enables customers to set up workflows, design and activate business event monitors, and manage tasks and alerts across products. |
Query Builder | Infor’s search tool for documents which uses Xquery. Can search for document attributes and properties, search for text within a document, and make your own advanced queries. Searches can also be saved by the user for quick access later. |
IDM Tools
IDM Utilities | The IDM Utilities tool is a self-contained executable JAR file containing multiple functions allowing you to import, export, and update data in IDM. Very useful for tech savvy users and for handling large amounts of documents. |
Microsoft Outlook Add In | Users can upload email attachments directly into IDM from Outlook. |
Microsoft Word Add In | Users can develop a template in Microsoft Word to be used in IDM Output Management. Can also search for images in IDM and insert into templates. |
Infor Mobile App | Utilize IDM capabilities on a mobile device, allowing the user to view, upload, search, and manage documents. |
DocuSign | Combines DocuSign’s capabilities with IDM, allowing users to lock documents, create DocuSign templates, and distribute documents to be signed and sent back. |
Enterprise Print | Users can register locations and associated printers to send IDM documents to be printed In that location. Allows you to print over the cloud. |
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference:
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out the IDM Cheat Sheet.
Topical Videos
Need information on a specific feature or function? Or how about a quick overview? Then short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand guides, see the following:
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in this component’s online community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers learning tracks that combine video-based and instructor-led teaching. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Document Management
Governance, Risk and Compliance
Overview
Infor Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) is the foundation of a secure and compliant business. Infor GRC is a comprehensive approach to managing the risks, compliance, and governance of an organization. It involves the implementation of policies and procedures that ensure that the organization is adhering to applicable laws and regulations, as well as taking the necessary steps to protect its assets and operations. GRC also involves the assessment of risks to the organization, the development of strategies to mitigate those risks, and the monitoring of compliance with applicable laws and regulations. By implementing effective GRC processes, organizations can ensure that they are taking the necessary steps to protect their assets, operations, and business interests. Here is an Overview of the Infor GRC Product.
Key Concepts & Definitions
GRC (Governance Risk & Compliance) | GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) is a process used to ensure that organizations manage their business in accordance with regulatory requirements and meet their internal objectives for risk management, operations, and performance. |
Governance | The process of implementing policies and ensuring that they are executed. |
Risk | The process of reducing risk and uncertainty through the establishment of business objective and governance mechanisms. |
Compliance | Adhering to the business rules, policies and guidelines whether they are internally or externally implemented. |
Application Instance | Are the connections between the Infor GRC application and the Data lake. |
Insights | Include the definition to classify the data to be monitored in an application. |
Tasks | Is an execution of a process in the Infor GRC application. |
Schedule | Is the functionality in the GRC application to analyze data and the certification process. |
Provision | A request raised for the User Provisioning. A provision can include a user creation or modifying the access for a user. |
Rule Book | Are a collection or group of rules. |
Rules | Include one or more conditions to identify risks in a business process. |
Conditions | Is a definition of a business process or a business activity. The conditions are the part of a rule. |
Violations | Are generated when data from an application is analyzed based on the predefined conditions in a rule. |
Mitigation | The Infor GRC function that enables the user to resolve the violations. |
Compensating Control | Documents that contain the business justification, the processes or agreements that are used for mitigating rule violations. |
Approval Process Template | Consolidates the stages and the approval process conditions to define an approval process. |
Component Parts
What Risk does GRC Address?
Infor Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) is designed to address a variety of risks, including financial, operational, legal, and reputational risks. GRC helps organizations to identify, assess, and manage risks associated with their operations.
Infor GRC Capabilities
Infor Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) provides organizations with a range of capabilities, including risk assessment, policy management, compliance monitoring, and incident response. GRC helps organizations to identify and assess risks associated with their operations, develop strategies to mitigate those risks, and monitor compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
GRC Workspace
The Infor GRC Workspace is a centralized hub for accessing the various GRC tools and services. This page provides users with easy access to the GRC tools, resources, and support they need to implement and maintain a secure, compliant, and well-governed business.
- The Infor GRC User Library is a collection of resources and tools designed to help users get the most out of their GRC experience. This library provides users with access to a variety of GRC-related documents
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There are numerous valuable resources available to enhance your understanding of the Infor Platform. One of the most helpful tools is a quick reference sheet, which can provide a concise overview of key information. You may find the following Cheat Sheet particularly useful for your learning and reference purposes.
Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature, function or a quick overview? Then short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Written Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see this component’s documentation:
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in this component’s online community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Governance, Risk and Compliance
Integration with ION
Create a unified application topology using the integration hub in the Infor Platform.
Overview
Intelligent Open Network (ION) is part of Infor OS; the technology platform of Infor. Infor ION provides the flexibility you need to make an often-complex web of enterprise systems work together. ION contains an API Gateway for a full System Integration.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Before diving into building your workflows, the following table provides you with Workflow key concepts for better understanding each component of a Workflow.
ION | Intelligent Open Network. Part of the Infor OS technology platform. |
BOD | Business Object Document. An XML document based on standards from the Open Application Group Integration Specification (OAGIS). |
ION Desk | A business representation of complex company data for end user consumption. |
Monitors | Approval matrices contain rules based on parameter evaluation for the distribution of approval tasks. These matrices can be used from Workflow to define approval chains. |
Workflows | Workflow enables communication from an application to a user. For example, it presents a document for approval or prompts the user to perform a task using a particular screen of an application. |
Activation Policy | A business representation of complex company data for end-user consumption. |
Workflow Schedules | Approval matrices contain rules based on parameter evaluation for the distribution of approval tasks. These matrices can be used from Workflow to define approval chains. |
Business Rules | Approval matrices contain rules based on parameter evaluation for the distribution of approval tasks. These matrices can be used from Workflow to define approval chains. |
Workflow Elements
Task | A workflow step that creates an entry of the Task type in a user’s task list. The workflow suspends execution until a user has completed this task, and then moves to the next step in the flow. |
Notification | A workflow step that creates an entry of the Notification type in a user’s task list. The workflow continues execution after the notification is sent to a user. |
Decision Table | An automatic step to set the value for one or more parameters that are based on the evaluation of a complex set of conditions. |
ION API | A step to perform a call to an ION API operation. |
Start Workflow | A step to start another workflow. |
Loop Back | A part of the flow that is repeated. |
Subprocess | A part of a workflow model that can be expanded or collapsed in the modeler. |
Task Chain | A series of approval tasks that are sent to different people. An approval matrix is used to model who should approve. |
Set Parameter | An automatic step to change the values of parameters. |
Exit Point | Exit point to implement custom logic outside the workflow. |
Wait | A step to let the workflow execution wait for a specified amount of time or until a specified date and time. |
Decision | An evaluation of a condition that has two possible follow up branches: Yes and No. |
Parallel | An unconditional execution of two or more execution branches in parallel. |
Parameter Data Types
String | Alphanumeric and Special Characters with a maximum length of 4000 characters. |
Decimal | A number that includes a decimal point. |
Date | Contains a date value. |
Code | A string having a value selected from a Code Table. |
User | A string containing the personid of an IFS user. |
Integer | A (64 bit signed) whole number. |
Boolean | True or False. |
Date and Time | Contains a date and time value. |
Hyperlink | A number that include a decimal point. |
DistributionGroup | A string containing an IFS distribution group. |
ION Connect
The main purpose of ION Connect is to deliver business documents from one place to another. With ION Connect you can establish connections between applications, both Infor applications and third-party applications.
You can configure ION Connect through the ION Desk. In ION Desk you can model document flows between applications. Such flows can represent a business process, but also more technical flows can be defined. For example, to map data from a third-party application to a standard business object document as used by an Infor application, you can also use filtering or content-based routing.
From the ION Desk, you can deploy your models to the ION Service by activating them. The ION Service will then make sure that documents are handled in accordance with your activated models. ION Desk also provides management screens to monitor the behaviour of the ION Service and to help in troubleshooting when needed.
Watch the video below for a full example of integration using ION Connect
Pass-through (Proxy)
The API Gateway receives requests from clients and delivers them to the proper target API. Clients know and invoke only one baseURL endpoint even if the target API can be different between the request and the response you can do other activities in the API Gateway for example applying policies for transforming or modifying the payload and the header of the request/response.
Orchestration
To reduce the complexity and management of invoking multiple different APIs, you can use the ION API Flow. Note that the ION API Flow is different compared to Document Flow and/or Data Flow, it is composed only of the ION API connection point plus decision components. You can define your own input parameters and output parameters and invoke multiple and different APIs, and the response of one API can be used as input for another API. After the design, you can deploy the ION API Flow that generates an endpoint in a dedicated API Suite (API Flow suite) that can be invoked by a client who provides one input and receives one output no matter the number of API calls done internally.
Hybrid
The ION API Gateway is a cloud-based service where you can host all public APIs and Infor products APIs. With the Hybrid service, we gave you the possibility to expose an internal API over the internet protected with the OAuth2 security. The only requirement is the Enterprise Connector which is the bridge between your internal API and the cloud
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There are numerous valuable resources available to enhance your understanding of the Infor Platform. One of the most helpful tools is a quick reference sheet, which can provide a concise overview of key information. You may find the following Cheat Sheets particularly useful for your learning and reference purposes.
Topical Videos
Seeking details on a particular feature or want a brief summary? These concise videos might be exactly what you need.
Written Guides
Product documentation serves as the primary reference for understanding specific product functionalities. For online, searchable, and user-friendly resources, refer to the following documentation.
Infor OS documentation Infor ION API Administration Guide API Gateway documentation BaaS documentation
Community
Collaborating with peers in your sector offers a valuable opportunity to learn and assist others. Dive into the Infor OS Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component: Infor OS Platform: Foundation for Multi-Tenant – Part 1Infor OS Platform: Foundation for Multi-Tenant – Part 2 Infor OS Platform: Configuring ION Connect Infor OS Platform: Configuring and Administering the API Gateway Infor OS Platform: Using Advanced Monitors and Workflows
Written Guides
Product documentation serves as the primary reference for understanding specific product functionalities. For online, searchable, and user-friendly resources, refer to the following documentation.
Community
Collaborating with peers in your sector offers a valuable opportunity to learn and assist others. Dive into the Infor OS Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Integration with ION
Portal and Workspaces
Overview
The Infor OS Portal is an advanced application framework offering a unified user interface for integrated Infor ERP applications. Within this portal, the navigation panel gives users access to various elements, notably the navigation menu which showcases the ERP applications. Furthermore, the smart panel, a foldable tray, houses both contextual and non-contextual widgets. These widgets dynamically present content enhancing user efficiency.
To tailor their experience, users have the ability to customize Workspaces and create shortcuts to their most accessed application screens and widgets. Beyond this, the Infor OS Portal boasts a drill-back capability, facilitating seamless navigation between applications. Users can navigate from one application to another to track transactions, transfer data, and report updates.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Infor OS Portal | A user-friendly, web-based platform that allows users to interact with a range of Infor applications, widgets, and tools from one central hub. |
Drillbacks | A mechanism by which we create links from one Infor Application to another while running inside Portal. |
Widgets | A single-purpose applications that provides at-a-glance information or quick access to interactive function. |
Workspaces | Infor OS is enhanced with focused views that provide users with streamlined experiences tailored to specific applications, tasks, and widgets, leading to improved usability and efficiency. |
Configuration Management | A functionality within the Infor CloudSuite Self-Service Portal (CSSP) and certain Infor applications that allow configuration and settings to be copied from one of your company’s tenants (e.g. TST) to another of it’s tenants (e.g. PRD). |
Bookmarks | Tools that serve as saved reference points, enabling quick navigation or access to specific and essential pages within Infor OS. |
Applications | The application management feature in Infor OS allows users to control all applications. It offers the ability to add, edit, or delete different application types, such as Infor Provisioned Applications, Infor Non-Provisioned Applications, and Non-Infor Applications. |
Smart Panel | An innovative feature that dynamically consolidates a user’s action items from various areas within Infor OS, presenting them in a centralized location to deliver timely and contextually relevant information. |
Tabs | Allowing for simultaneous viewing of multiple workspaces, users can keep them open concurrently. |
User Settings | Settings refer to the customizable global preferences in a system that include options for language, locale, time zone, and themes.advanced queries. Searches can also be saved by the user for quick access later. |
Widget Types
Published | You can publish a widget to the Widget Catalog to make it available to other users. |
Insight | An insight is like a small widget page contained within the smart panel. |
Standard | The Standard Widgets page displays a listing of all standard widgets created by the application teams. |
Tenant | A tenant widget and a standard widget could be very similar, but the tenant widget id will always start with “tenant.“ while the standard widgets starts with “.infor“ |
Widget Catalog Types

Workspaces Types
Private | For that specific user only. The user is usually allowed to edit these workspaces |
Published | When you publish a private workspace to the Workspace Catalog, the page becomes a published workspace. |
Standard | The Standard Workspaces page displays a listing of all standard workspaces created by the application teams. |
Dynamic | Available in the catalogs for users to add, but can show different content for different users. |
Infor OS Portal Diagram
This diagram provides a detailed illustration of the diverse components that come together to shape the user experience. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless and intuitive interaction for the user.
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
Explore the Infor OS Portal for a wealth of knowledge. Dive into the product overview for valuable insights.
Topical Videos
Seeking details on a particular feature or want a brief summary? These concise videos might be exactly what you need. Take a look at our Infor OS Portal playlist on YouTube.
Written Guides
Product documentation serves as the primary reference for understanding specific product functionalities. For online, searchable, and user-friendly resources, refer to the Infor OS Portal documentation.
Community
Collaborating with peers in your sector offers a valuable opportunity to learn and assist others. Dive into the Infor OS Portal Community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers Learning Paths that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, check out courses on Infor U Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Portal and Workspaces
Robotic Process Automation
RPA automates repetitive tasks and empowers your team to focus on what they do best.
Overview
Infor Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a set of software components that provides the ability to automate business processes with the help of Bots to perform a sequence of meaningful activities that can mimic human behavior or perform other system activities.
Infor RPA also includes the cloud-based Multitenant component called the Mastermind, which orchestrates and allows the deployment of the workflow processes, configuration, scheduling, and monitoring capabilities.
Key Concepts and Definitions
RPA | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots or bots to automate rule-based, repetitive tasks in business processes, reducing manual effort and human error. |
Bot | A bot or robot in RPA refers to the software program or agent that performs tasks in an automated manner. It can mimic human interactions with computer systems. |
RPA Flow | A sequence of activities or steps that an RPA bot follows to complete a specific business process. |
Process | A list of all published RPA flows. |
Job | An execution instance; it is specific to a Process. |
Device | A physical machine where the agent (which executes the RPA process in unattended mode) is installed. |
Orchestration | The management and coordination of multiple RPA bots and processes to work together seamlessly, often through a central control system. |
Attended Mode of Execution | Attended automation involves bots working alongside human operators to assist with tasks in real-time. |
Unattended Mode of Execution | Unattended automation runs independently without human intervention, often in batch processing mode. |
Key Components
RPA Studio | A desktop application that Infor Employees, Customers, and Partners can use to build workflow processes for their business use cases. Studio allows workflow authors to design, develop, and publish RPA Processes. |
RPA Mastermind | An Infor RPA Engine that communicates between the on-premise installation and Multi-tenant cloud RPA Management to trigger the run of RPA processes. |
Agent Runtime and Robot Service | Desktop applications installed as part of unattended installations.- Agent: A Windows service that communicates with Mastermind and processes automation requests configured by the user in the RPA Management UI in an unattended mode.- Runtime: Executes the workflow processes that users have authored in Studio.- Robot Service: Communicates with the Agent inside a Windows user session and triggers Runtime. |
RPA Management API | A multitenant microservice deployed in the cloud that serves as the backend entry point for the RPA Management UI, Agent, and Tray Assistant. |
RPA Management UI | A multitenant application hosted in the Infor OS Portal. Provides a user interface for RPA users to add extra configuration for their workflow processes, including:1. Job configuration (scheduling, device assignment)2. Adding variable values3. Giving consent for workflow processes to access resources behind IONAPI4. Device registration5. Robot registration (Windows login credentials for automation)6. Task Monitoring |
RPA Tray Assistant | A desktop plugin application installed to execute processes in an attended mode.1. Gives users control to automatically trigger any of the workflow processes they have access to in Mastermind.2. Add variable values.3. View workflow process details. |
Recorder | A Chrome-based extension allowing users to record a set of activities in the Chrome browser, generating an RPA flow of activities. |
Workflow Elements
IDP | Infor Document Processor is a service designed to recognize and extract text from images or documents. |
JQ Transformation | JQ is a JSON processor used to slice, filter, map, and transform JSON data with ease. |
JSON To DataTable | Takes a flat JSON array containing the required columns for transformation and outputs a DataTable. |
ForEach | Executes the activity contained in its Body for each item in a specified Values collection. By default, the loop iterator is named |
Try Catch | An exception-handling activity that works in conjunction with the “Continue on Error” property of the activities. If |
GET OCR text | An automation activity in RPA Studio that extracts text from documents or images. |
Extract Document Key-Value | An automation activity in RPA Studio which extracts values based on provided keys. |
Extract Data | An automation activity in RPA Studio that can perform template-based text extraction. |
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Technology Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out this RPA Cheat Sheet.
Topical Videos
Need information on a specific feature, function, or a quick overview? These short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our Infor Robotic Process Automation playlist on YouTube.
Written Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy-to-understand docs, see our documentation portal.
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in the Infor RPA Community today.
Courses
Infor U Campus offers learning tracks that combine video-based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer, then check out courses on Infor U Campus.
Written Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see our documentation portal.
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in the Infor RPA Communitytoday.
Courses
Infor U Campus offers learning tracks that combine video based and instructor-led training. If you are an Infor customer then check out courses on Infor U Campus.
On this page
- Robotic Process Automation
Security & User Management
Tutorials that help you leverage Infor's cloud security and user management capabilities.
Infor Cloud Identity & Access Management is where Infor User Management and access will be handled by IFS (Infor Federation Service) along with the Infor Federated Hub for the Authentication and Authorization of User Account Management. This component of the Infor Platform is utilized by those accessing the Infor Cloud from a browser based app, mobile app, or API.
An Overview of how Infor Federated Services (IFS) facilitates the management of users and permissions.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Access management is the process of managing a user’s login and access across a wide range of applications, systems, and resources belonging to an organization. IAM services authorize user access to protected resources, but delegate the authorization decisions to the applications’ owners. |
Identity Provider (IdP) | A system that validates the identity of a user in a federated system. The service provider (or SP; see below) uses the IdP to get the identity of the current user. |
Service Provider (SP) | A system that provides a generic service to the user in a federated system. To users, a service provider is the same thing as the application they are trying to use. |
Federation | An agreement ( trust ) between identity providers and service providers that allows for the sharing of information. It lets users of a service sign on to said service through one single identity provider. Also known as federated identity management, this is a technical implementation that enables identity information to be developed and shared among several entities and across trust domains. |
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) | SAML is an industry standard XML-based framework for communicating user authentication and attribute information. The SAML 2.0 protocol standard is leveraged by Infor applications |
Single Sign On (SSO) | A service model in which users log into one single platform that gives them automatic log-in access to multiple applications for a certain period of time. Users using this system only have to remember one set of credentials, as opposed to learning a new password for each application. |
Single Log Out (SLO) | Enables a user to log out of all participating sites in a created session. The party that authenticated the user handles all logout requests and responses for participating sites. |
Identity Stores | User information stored across a variety of technologies, including databases, LDAP, Active Directory, etc. |
User Provisioning | A set of technologies that create, modify, and de-activate user accounts and their profiles across IT infrastructure and business applications. |
System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM) | SCIM is a standard for automating the exchange of user identity information between identity domains, or IT systems. SCIM communicates user identity data between identity providers and service providers requiring user identity information. |
Just In Time (JIT) | Process where a user account can be created on demand after successful authentication occurs. |
Authentication | Authentication is the process of validating an identity, whether it be the identity of a user or, as in the Identity of Things, a device. The classic method of validation is the username/password combination. Authentication ensures that the individual is who he/she claims to be. |
Authorization | The process of determining if a user has the right to access a service or perform an action or the process of giving individuals access to system objects based on their identity. |
Component Parts
Single Sign On (SSO) Overview
User authentication process that authenticates the user for all the applications they have been given rights to and eliminates further password prompts.
Authentication and SSO details
- Infor OS in the cloud leverages Infor Security Token Service (InforSTS) as the identity provider used for authentication.
- Infor Federation Services (IFS) is the identity store, users requiring access to Infor OS Cloud must have a cloud identity account.
- InforSTS is a SAML 2.0 complaint identity provider.
- Infor applications existing in the Infor Multi Tenant cloud will be integrated with the Portal Federation Hub in order to achieve SSO. The Portal Federation Hub is the interface designed to allow authentication flows between applications and InforSTS. Once a user authenticates to the Infor Cloud portal they will have access to all other applications without being challenged for credentials due to the token supplied by the Portal Federation Hub to the user browser session.
- Infor Cloud is SP initiated SSO, user accesses the Infor Cloud portal and is redirected to the identity provider if authentication is required.
SSO Options
- Infor OS Cloud can be federated with other identity providers to allow for authentication and SSO from other sources, typically this would be done to grant customer accounts access to the Infor OS Cloud portal and eliminate the need to create and maintain cloud identity accounts for users.
- Federations can be created with any SAML 2.0 capable identity provider.
- Infor OS Cloud now supports Open ID Connect which relies on the OAuth 2.0 protocol for federations.
- Federating with identity providers provides flexibility for customers on the identity providers used and the identity stores used by those identity providers.
- ADFS SAML Federation with Infor CloudSuite
- Azure AD SAML Federation with Infor CloudSuite
- Azure AD OIDC Federation with Infor CloudSuite
- Google G-Suite SAML Federation with Infor CloudSuite
- Okta SAML Federation with Infor CloudSuite
- Okta OIDC Federation with Infor CloudSuite
Authorization and IFS Overview
- After authentication occurs access to the Infor OS portal requires authorization. This is handled by Infor Federation Services (IFS), this is Infor’s user management application.
- In order to be authorized a user must have an account within IFS.
- In order to access applications a user must have security roles assigned to their account. These security roles are defined by application and functions within the applications that exist within the Infor OS portal.
- Some applications rely solely on IFS for security purposes and some Cloudsuites have their own security in addition to IFS security roles. In order for a user to access these applications they would require the correct IFS security roles for the application and would need to have an account within the specific application in order to gain access and run features and functions.
- Access to the Infor OS portal requires authentication and authorization, both have equal importance when it comes to application security.
User Provisioning – Cloud
- Infor OS Cloud does not have the ability to bind to an Active Directory like the on-premise version.
- Users can be manually created within the IFS user management application. When a user is created, they will be sent an email asking them to verify their account and to create a password for that account.
- Other user provisioning options are manual import of user information from a CSV or XML file.
- SCIM can be used to publish or get user information between a SCIM capable application and Infor OS Cloud. Infor OS is SCIM 1.1 and 2.0 compliant. Infor OS Cloud has SCIM service only capability.
- If Infor OS Cloud is federated with another identity provider, then the requirement to have a user verify their account and create a password is not needed. The option to generate the verification email when users are added to IFS can be turned off.
- If Infor OS Cloud is federated with another identity provider, then there is an option to use Just In Time (JIT) to have user accounts created on demand.
- Users can also be provisioned to IFS via a Security User Master ( SUM ) BOD (Business Object document) generated from another application that has a user repository and supports BODs. Infor GHR is an example of a cloud application that generates a SUM BOD that IFS can consume for user provisioning purposes.
Authentication and Provisioning Flow
The Authentication and Provisioning flow diagram illustrates the configuration and flow of the Federation (Authentication) and User Provisioning (Authorization) to a Identity Provider using SCIM for user provisioning automation and maintenance.
SCIM User and Security Role Flow
The SCIM User and Security Role flow diagram illustrates how SCIM groups are used to assign security roles to IFS users using the Azure AD identity provider SCIM interface.
GHR CSV Integration Diagram
The GHR CSV Integration Diagram illustrates how user provisioning can be automated from the GHR application source of record to a customers corporate HR application system using a CSV file format.
GHR API Integration Diagram
The GHR API Integration Diagram illustrates how user provisioning can be automated from the GHR application source of record to a customers corporate HR application system using a API call.
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out the IFS IAM User Management Cheat Sheet.
Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature, function, or a quick overview? Then short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Written Guides
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see this component’s documentation:
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in this component’s online community today!
Courses
Infor U Campus offers learning tracks that combine video-based and instructor-led teaching. If you are an Infor customer, check out courses on Campus. We recommend the following courses specifically for this component:
On this page
- Security & User Management