Overview
Tutorials are designed to offer a guide to complete common objectives, while also acknowledging that individual developers need to respond to individual needs of their own solutions. Tutorial frameworks provide blueprints for these solutions and should be adapted to fit individual needs.
Analytics with Birst
API Gateway
Application Development with Mongoose
Artificial Intelligence
Data Fabric
Digitical Assistant
Document Management
Integration with ION
Robotic Process Automation
Add description here
Security & User Management
Add description here
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Overview
Analytics with Birst
On this page
- Analytics with Birst
API Gateway
API Gateway is a software system for brokering requests from API consumers, such as web and mobile applications, and API providers, such as Infor enterprise or third-party services. As a broker sits between consumers and providers (technically it is a reverse proxy), it can provide many benefits to both consumers and providers.
On this page
- API Gateway
Application Development with Mongoose
Go beyond basic fit and customize your cloud experience with extensibility tools that leverage no-code, low-code, and full-code frameworks.
On this page
- Application Development with Mongoose
Artificial Intelligence
Use Machine Learning to build an AI into your business processes.
Machine Learning (ML) is a category of Artificial Intelligence (AI), computer science, and mathematics that focuses on using data and algorithms to train models and use those models to make predictions on new and unseen data. Infor AI opens up the world of machine learning to a wider array of business users through its visual modeler, allowing for deployment of models with low-code and no-code implementations.
Key Concepts & Definitions
Infor AI | Infor’s machine learning platform, a component of Infor OS. |
Quest | A flow of activities that make up the machine learning model. |
Training Quest | A quest involving a predictive method that produces a trained model. |
Trained Model | A model that can be used to predict outcomes based on new data. |
Production Quest | A trained model that has taken steps to deployment. |
Endpoint | The REST API access point of a real time production quest to process new data through the model. Endpoints can process data by being passed a CSV, a JSON message, or accessed via the API gateway. |
Data Lake | Flexible and economical cloud object storage solution where data is stored in its raw format. This is Infor AI’s primary data source. |
Label/Target | Terms that refer to the prediction of the model. |
Categorical | Data types that are non-numeric in nature and belong to a category instead. E.g. “Country of Residence”. |
Supervised Learning | Machine learning algorithms that form relationships between targeted label and input features so that the output values for unseen data can be predicted. Supervised algorithms must be trained on known outcomes. |
Unsupervised Learning | Machine learning algorithms that make inferences from data using only input features without referring to known or labelled outcomes. These algorithms can discover data structures by clustering it into intuitive groups. |
Best Practices
A machine learning project has a lot of flexibility and user control over it, but it is generally accepted that an ML workflow adopt the product life cycle below.
Business Case Definition
Before starting a machine learning project, it is best to step back and define the business problem at hand. It takes some finesse to match business problems with the appropriate algorithms, and the appropriate data. Often, business problems fall into one of the following categories.
Fetching Data
The enterprise can produce incredible amounts of data from different systems. For use in the Infor AI platform, data should be managed and stored in the data lake.
Data Preparation
Data preparation tasks can be numerous and time consuming. It is recommended that one be familiar with tidy data standards when it comes to cleaning data. It is also important to understand any caveats to the particular algorithm that you might use to process the data. Infor AI has the following built in tools for data manipulation and preparation, as well as the ability to run python scripts to allow for complete customization when manipulating data.
Select Columns | Select or exclude a subset of columns from the current dataset. |
Remove Duplicates | Remove duplicates in selected features. |
Construct Feature | Create a new feature out of the existing ones by using mathematical, logical, or casting operations. |
Index Data | Transform categorical values into numeric for the selected columns. Each category will be assigned a number according to its occurrence in the data, highest occurrence having number 0. |
Smooth Data | Remove noise from a dataset to allow natural patterns to stand out. |
Split Data | Split the dataset into training data and test data by specifying the split ratio for the training dataset. |
Scripting | Execute a customized Python script to perform an activity which is not available in the catalog. |
Ingest to Data Lake | Ingest data to Infor Data Lake |
One Hot Encoder | Transform categorical features into a binary matrix (vectors) to distinguish each categorical label. The vector consists of 0s in all cells, with the exception of a single 1 in a cell used uniquely to identify the label. |
Feature Scaling | Scale features with varying magnitudes, units and range into normalized values. |
Handle Missing Data | Replace missing values in selected features (with mean / mode / constant value / interpolation), or remove the entire row exceeding a selected ratio of missing data. |
Target Encoder | Numerization of categorical variables via target – replaces the categorical variable with just one new numerical variable and replaces each category of the categorical variable with its corresponding probability of the target (if categorical) or average of the target (if numerical) |
Edit Metadata | Select the Target label. Edit the metadata of the selected features by changing its data type, tagging the categorical values, changing the variable name or defining their machine learning type. |
Balance Data | Balance the dataset using undersampling or oversampling methods. |
Execute SQL | SQL operations (filter out data, join datasets, aggregate data etc.). |
Model Training
Training a model requires the prepared dataset and the algorithm to be used in training. Supervised algorithms can be scored for accuracy using the train/test split functionality and the score and evaluate model blocks. The compare model block will allow for the training of multiple models to compare performance statistics.
Model Fitting & Tuning
Algorithm hyperparameters are available in each of the algorithm blocks. The specific parameters will be different depending on algorithm selection, and can details for each hyperparameter can be found in the documentation of the chosen algorithm.
Model Deployment
In the quest, select the checkbox on activities desired for the deployed model and push the activities to the production quest. This quest can be deployed as an endpoint accessible via the ION API gateway.
Model Maintenance
Want to learn more?
Quick Reference
There is a lot to learn in the Infor Platform. A quick reference sheet is always helpful. Check out this Cheat Sheet.
Topical videos
Need information on a specific feature or function? Or how about a quick overview? Then short videos may be just what you are looking for. Check out our playlist on YouTube.
Product Documentation
Product documentation is the go-to reference for how specific parts of the product work. For online, searchable, easy to understand docs see this component’s Documentation.
Community
Collaborating with others in your industry is a great way to learn and help others. Start participating in this component’s online Community.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Artificial Intelligence
Automated Retraining
Overview
Machine learning models are trained with data fed into them during training. Data itself is more dynamic as business conditions, economies, and sales data change rapidly. Having your models periodically, and automatically, retrain with up-to-date data will keep them from becoming stale -- ensuring that their prediction accuracy does not weaken over time.
This tutorial will cover how to set up automated retraining of your machine- learning models.
Components
- Machine Learning: Infor AI * System Integration: ION Desk * Data Fabric: Data Lake
Requirements
- Access to an Infor CloudSuite * Infor AI Security Roles: * COLEMANAI-User * COLEMANAI-Administrator * User privileges to ION workflow * An AI quest that: * Draws data from Data Lake * Runs successfully * Has a deployed Endpoint * A dataflow that updates the data in the Data Lake
Tutorial
Difficulty: Easy Time estimate: 30 minutes
In this tutorial, we will create a workflow in ION that will periodically run an automatic model update for the desired Infor AI model. Before we get started with the actual workflow, we will need to download the service account credentials
In order for ION Workflow to later call the Infor AI API a service account must be created.
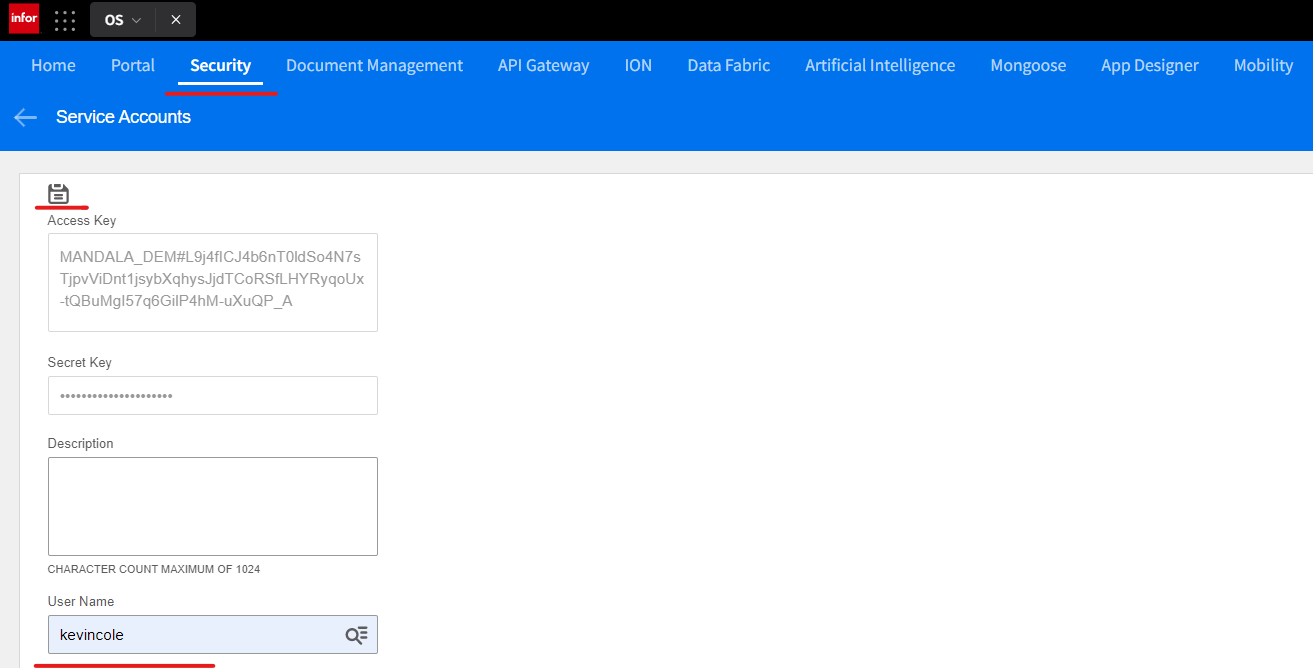
1. Service Account Credentials Download
- Navigate to the security section of Infor OS. Use the menu on the left (hamburger menu) and go to Manage > Service Accounts * Click the + for Add new item * Add your username to the username field * Save the Service Account Credentials locally with the save icon. It will download a CSV file named "Service Account" that includes the tenant name and a unique identifier.
2. Navigate to ION
Automated retraining will take place in Infor ION. Navigate to ION in Infor OS and using the side menu select Monitors & Workflows > Workflows.
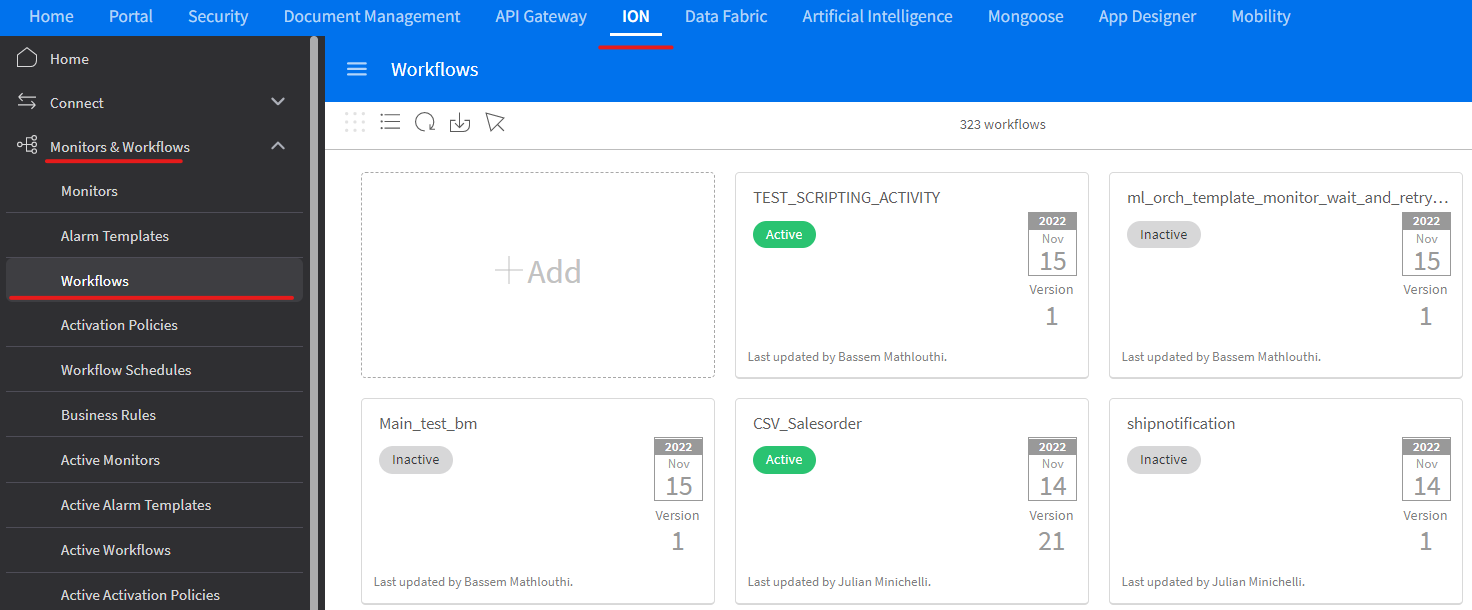
3. Create a new workflow
Use the interface to create a new workflow by clicking +Add. Certainly, you could add these steps to larger existing workflows, but we are going to model this in a new workflow that will just be focused on the retraining.
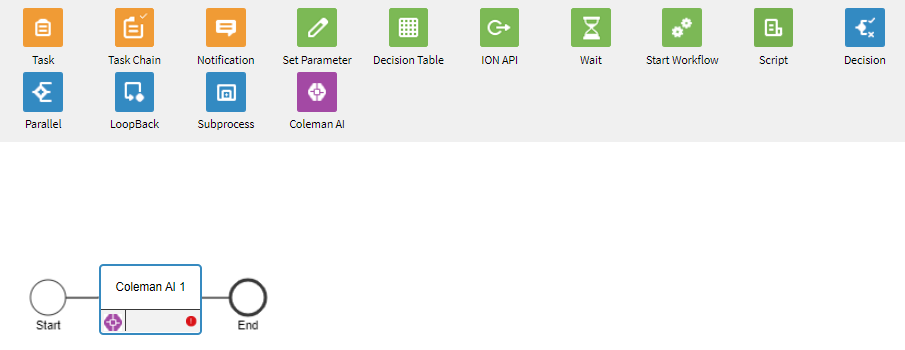
4. Add AI Task
Drag the AI task from the pool of available workflow activities to the workflow.
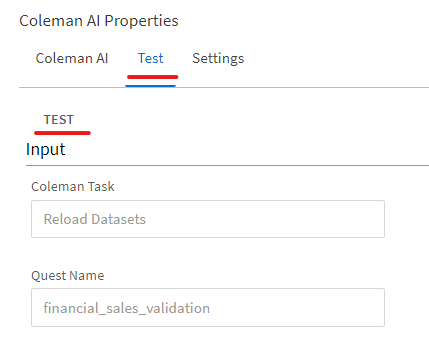
5. Settings
Click on the AI block to access its properties. In the AI task dropdown, select "Reload Datasets" for the first activity. Identify the quest name and import the service account file we created in step one. The quest name serves as the identifier for all activities, so even if you are reloading data sets select the quest that those datasets are called from. Rename the activity as appropriate.
6. Test Configuration
Move to the "Test" hub and click the test button. This should tell you if the AI task, quest name, and service account are valid and agree with each other.
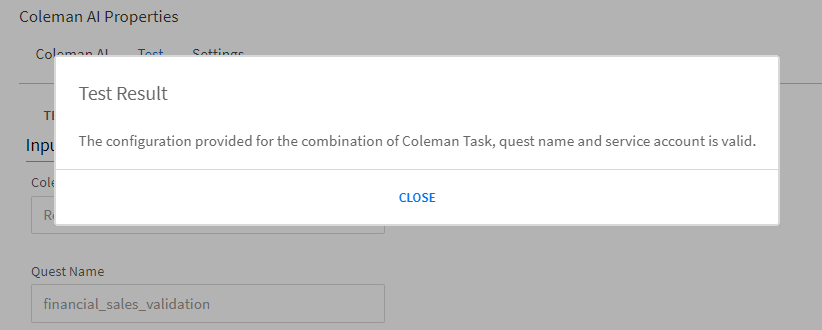
7. Error Handling
In the settings tab, specify how you want errors handled. You can optionally select to continue the workflow and send error messages, however, it makes more sense in the retraining case to select "The Workflow Fails", as it doesn't make sense to continue with retraining activities if the data has failed to update.
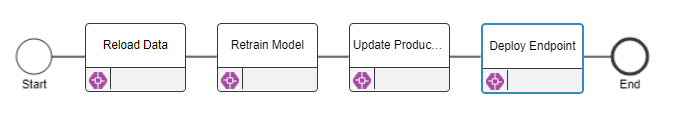
8. Repeat for each of the four retraining activities.
There are four options available in a AI task that appear in the dropdown. Executing these tasks in succession will complete a retraining cycle. Create one activity for each of the available tasks in this order:
- Reload Datasets * Retrain Model * Update Production Quest * Redeploy endpoint
Once completed, your workflow should look something like this, and the error/notification bubbles should all be resolved. Be sure to save the workflow.
10. Schedule retraining
Back in the left-hand ION navigation menu, under Monitors & Workflows, navigate to Workflow Schedules. Create a new workflow schedule with the "+Add" button and give it a name and description. Use the schedule panel to detail when you would like the workflow to run, and at what frequency. In the action panel, find the workflow you created above and select it in the dropdown. In the "Trigger Workflow Instance" dropdown, select skip if the workflow is running.
11. Activate
Using the toolbar at the top, save the workflow schedule and click activate. Your workflow is now configured for automated retraining and will trigger at the specified time. To verify that retraining occurred, examine the quest in Infor AI. There will be two locations that tell you the quest was triggered from ION Workflows, the quest tile on the quest home screen, and the status messages on the left-hand side of the quest when you open it.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Automated Retraining
Customer Segmentation
Overview
Treating all of your customers the same is not usually a great business strategy. Customers can be very different, but with large numbers of customers there are bound to be groups of similar ones. By segmenting a customer set into groups, business decisions can be made to address different types customers appropriately.
Scenario: A fictious big retailer chain operates a membership-model business where their customers pay an annual membership fee for access to their warehouse-like stores for great prices on bulk items.
Data: Being a membership business model, customer data is abundant in this scenario. Data includes demographic data on each customer, seasonal spending data, coupon history, and purchase history. This data is contained in multiple systems and multiple tables across the enterprise. There will need to be a data consolidation effort to prepare the relevant information for the machine learning model. We will walk through the implementation with this sample customer dataset.
Components
- Machine Learning: Infor AI * System Integration: ION Desk * Data Fabric: Data Lake
Requirements
- Access to an Infor CloudSuite * Infor AI Security Roles: * COLEMANAI-User * COLEMANAI-Administrator * Mall Customers download
Tutorial
Difficulty: Medium Estimate Time: 60 Minutes
Step 1: Create one or more dataset(s).
Using multiple datasets is perfectly fine, as your quest can refer to each dataset individually, get what it needs, and merge or manipulate data into its final form ready for the ML model. We will import this csv file for use with our sample, but your business data will likely live in the data lake.
https://youtu.be/M_hPQa_GcRU?si=BxCmrwmTFGOSIPwA
Here you can see Infor AI giving us a preview of the dataset.
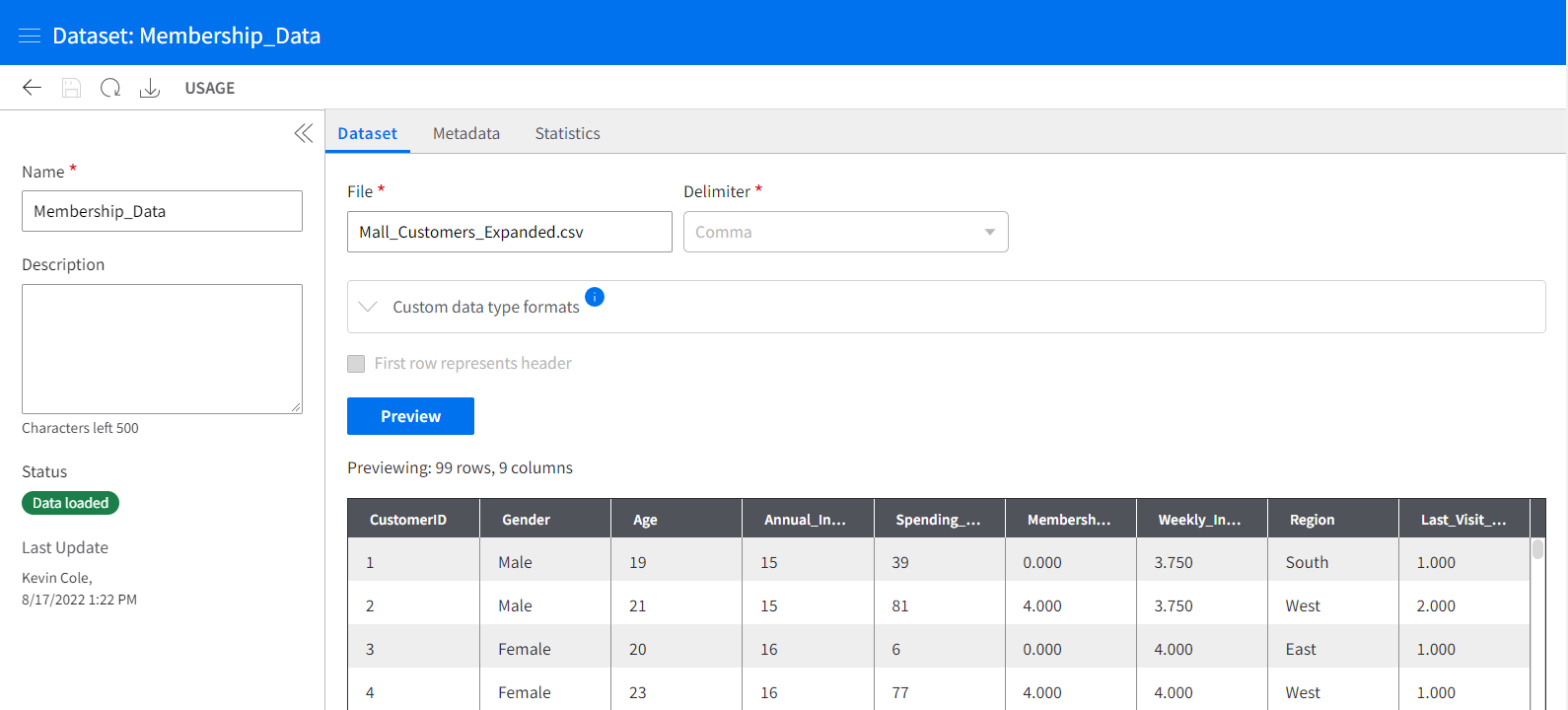
Step 2: Save the quest
In the Quests section of Infor AI, create, name, and save your new quest. This will create the blank canvas for your model to be developed.
Step 3: Import Data
Use an import data block, and within that block select the dataset you made in the prior steps. Once saved/run, you will be able to see the current state of the data at the output node on the right hand side of any given activity in the platform. Exploring your data will be important, as finding the oddities in the data now can help you know what prepare data steps are necessary. In my exploration of this sample dataset, I noticed the following:
- CustomerID is a unique identifier. It provides no information about the customer or their spending habits, and would not be a useful predictor of future behavior. We should not include CustomerID as a factor when creating customer groups or customers might be incorrectly grouped together because of their arbitrary position in the dataset. * Gender, and Region in this dataset, are nominal (non-ordered) categorical variables. Categorical variables will need to be encoded regardless of how many items are in the categorization. * Annual_Income and Quarterly_Income have a high correlation. In fact, Quartly_Income appears to be the Annual_Income divided by 4, creating a perfect correlation. You should avoid using both (all) when variable have a strong correlation, as it can overweight the importance of the feature. * Last_Visit_Weeks has missing values. We will need to address this before using the feature. This could be due to a new membership being created before the customer has used their membership.
Step 4: Cleanse data
Using the green prepare data blocks, you can engage in the data cleaning activities required to get your data ready for consumption by a model.

https://youtu.be/9OT5Oa7EX38?si=NsluGFRUUCcKwNVW
This blueprint addresses the bullet points in step 3 with the following decisions:
- CustomerID will be dropped * Gender and Region will be encoded with One-Hot-Encoding. Features must first be identified as categorical * Quarterly_Income will be dropped * Last_Visit_Weeks missing values will be set to zero.
Step 5: Select a model.
Understanding which model to use and what its unique requirements are takes a bit of subject matter knowledge.
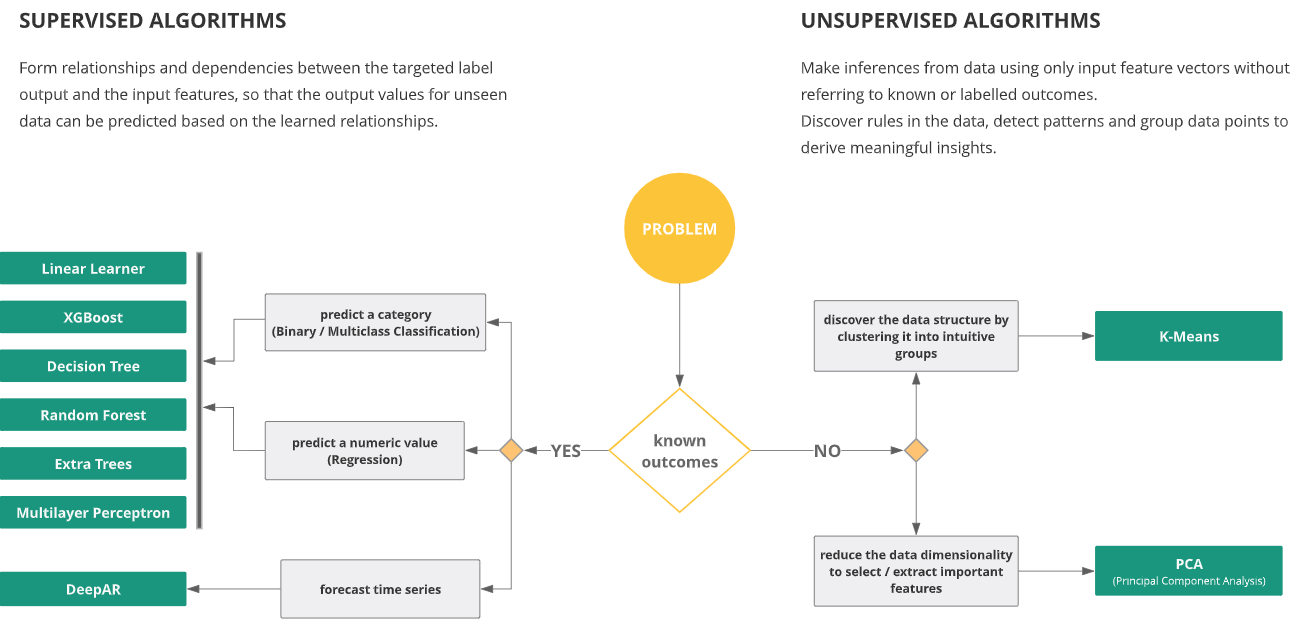
For the clustering project, we would select the K-Means clustering algorithm, or develop our own clustering algorithm using the custom algorithm functionality. Add the K-means block, or custom algorithm block to the quest.
https://youtu.be/0BHzyb5ekvE?si=pZlztr0BlHYNZN6m
Step 6: Set hyperparameters.
In the K-Means algorithm block, let the algorithm know how many columns you will be feeding it, and how many clusters should be created. You may optionally tweak other hyperparameters for performance tuning. This blueprint would set the Feature Dimensionality to 12 and K to 5.
Step 7: Train the model.
Use a train model block and pass in two inputs -- the data that has been prepared, and the algorithm chosen. The quest should resemble the image below.
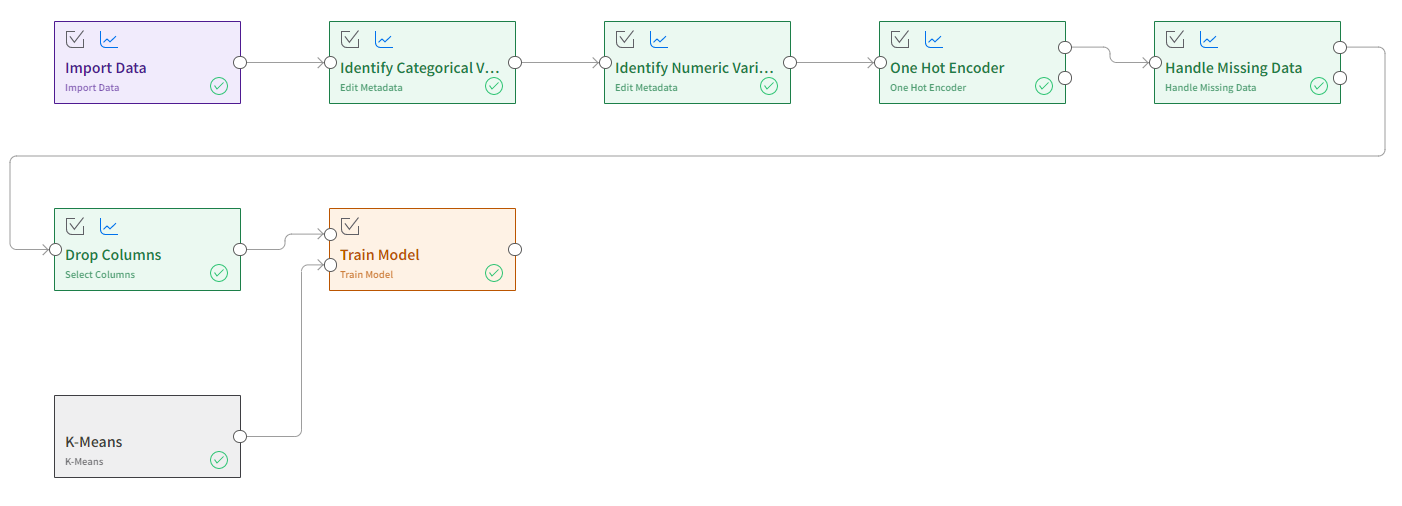
If successful, the node on the right of the train model block should contain information on the centroids of each cluster. These centroids don't have practical meaning, but are multi-dimensional locations that a customer will be found closest to.

Step 8: Score the model.
In this case, since the algorithm is an unsupervised learning application, there is no "truth" so accuracy metrics are not created, but giving the model the score model block will take the customers and assign each one to a cluster. The node on the right of the Score Model block will show the dataset and a new column identifying which cluster the customer belongs to.
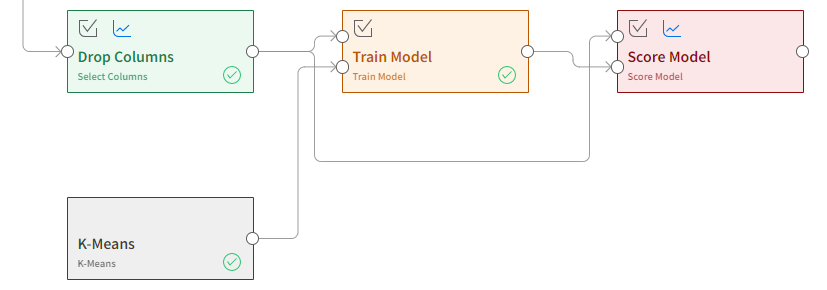
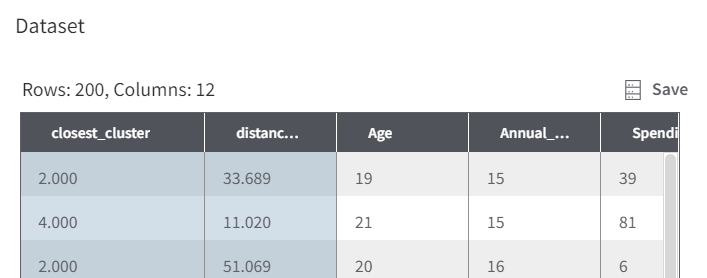
Step 9: Deploy the model.
At the right of the toolbar, there is a checkmark for Auto-selecting activities for real-time production. This is the option we will use if we wish to have a deployed endpoint accessible via API. The batch production would be a better option for handling a large dataset for a single processing task. After using the auto-selection tool, or making sure the checkbox on each activity in the quest is checked, save the quest, then create a production quest.

The production quest will look different, and that's okay. Save the production quest, run it, and you will then be able to deploy it as an endpoint at the right of the toolbar. Follow the prompts to name and deploy the endpoint.
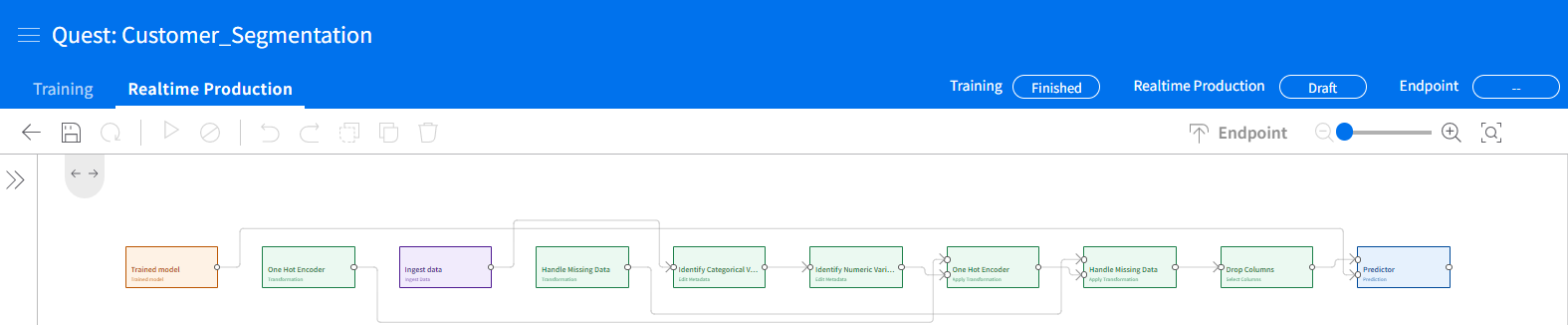
Step 10: Test the endpoint.
Navigate to the Endpoints section of Infor AI. Open your newly deployed endpoint and feed it some test data. This can be in the form of a file (CSV) or a JSON message as below. You can see that once a prediction is made, the endpoint returns two values, one is the integer value representing which customer group the new customer belongs to, and then a value representing the "distance" of that customer to the cluster center.
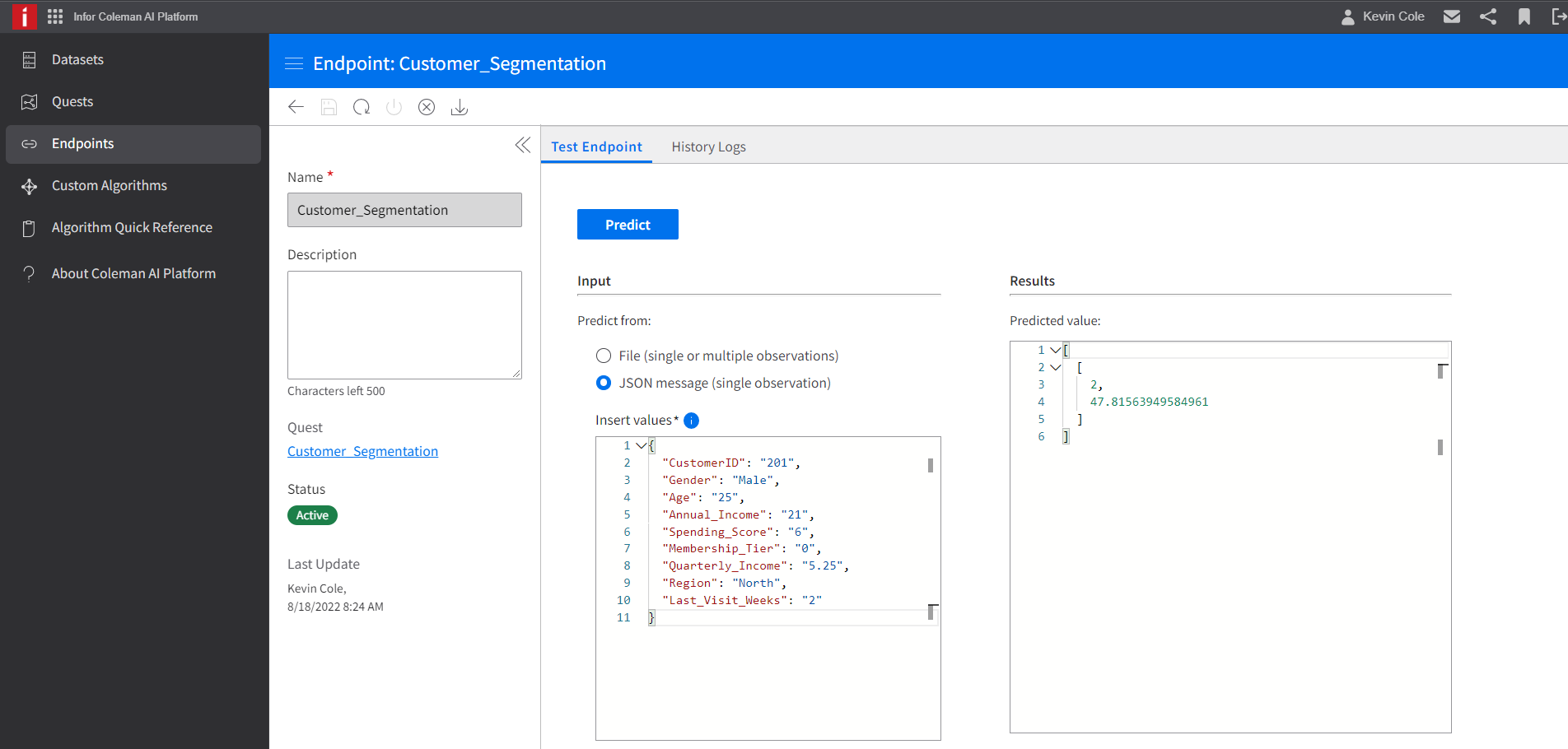
Step 11: Test the API
To access the endpoint via API, use the app switcher to navigate to Infor ION API, where you will find Infor AI Platform in the set of available API's. You can use this API endpoint to query the model from applications or widgets.
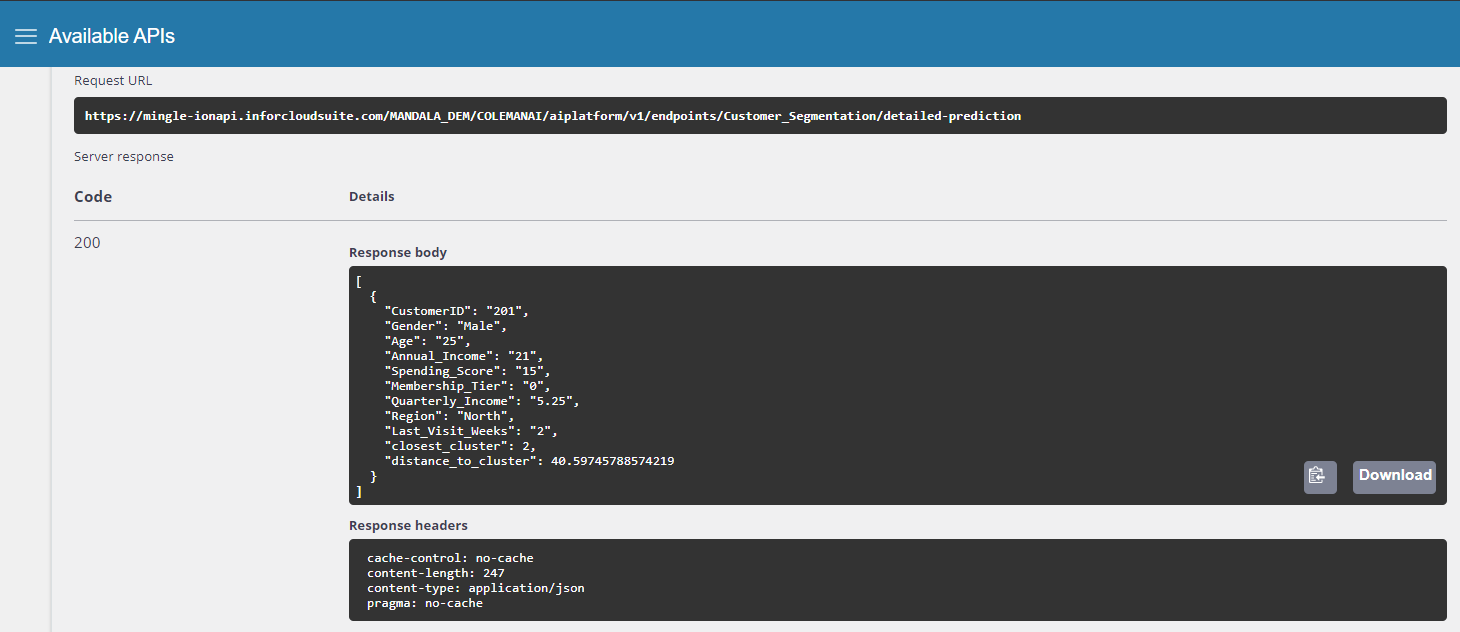
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Customer Segmentation
Implementing Custom Algorithms
Overview
Infor AI tools provide out-of-the-box algorithms that are common in machine learning. For various reasons, you have decided that the out-of-the-box models don’t deliver the functionality you are looking for, or you believe the performance can be improved on. Now, you wish to develop your own custom algorithm to improve your performance metrics.
Components
- Machine Learning: Infor AI
Requirements
- Access to an Infor CloudSuite * Infor AI Security Roles: * COLEMANAI-User * COLEMANAI-Administrator
Tutorial
Difficulty: Medium Estimated completion time: 20 minutes
Step 1: Choose your development environment
You may code in a local environment or workspace if you prefer. You’ll need to package the files according to the documentation in the instructions tab. If you have chosen to develop outside the platform, ensure you understand your requirements as described in the instructions tab. Otherwise, open the Custom Algorithms section and add a new custom algorithm from the home screen. Select “Open Notebook.” and give the algorithm a name before saving to enable the notebook.
A look at using Jupyter Notebooks in Infor AI seen here:
https://youtu.be/VBHsQ-A8rfI?si=cP5bIEmB5F8ylObT
Step 2: Understand your requirements
To create a custom algorithm, you must create two essential scrips and a set of hyperparameters. These items will be treated differently based on your choice in step 1. The scripts are:
- train: The program that is invoked to train the model * predictor.py: The program that implements the Flask web server that can be called to get predictions from the trained model.
Step 3: Understanding the interface
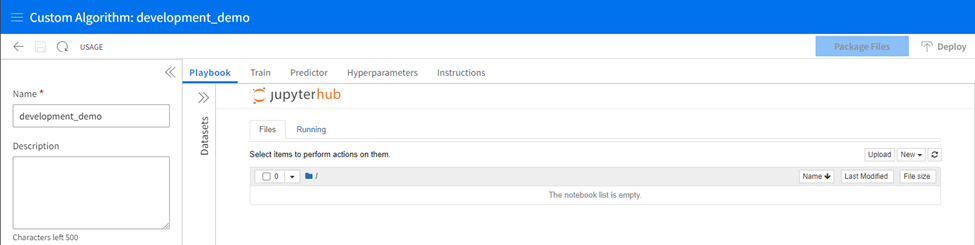
There are several areas of this interface in which your development will take place.
The Playbook:
The playbook tab is a non-required coding space where a Jupyter Notebook interface lets developers code and experiment with their development in a sandbox-style workspace. Creating a new notebook allows you the standard interface of a Jupyter Notebook. You can view the available Python packages and their versions with a “!pip list” command.
Train and Predictor Tabs
Train and Predictor tabs are spaces ready to receive the final train and predictor.py scripts for deployment. These spaces have no testing capabilities, so it is best practice to develop and test your scripts in the playbook tab and copy them to the train and predictor tabs when they are complete. The hyperparameters tab is where you will upload a CSV detailing the hyperparameters for your algorithm and their default values and types.
Hyperparameters Tab
The hyperparameters tab lets you individually add hyperparameters and their properties directly to the grid. You may optionally import a CSV with this information, which will then be displayed in the table and editable from there.
Datasets
The datasets section will expand from the left bar, allowing you to bring datasets already staged in Infor AI into the Jupyter Notebook environment.
Instructions
More instructions and sample files for easy access.
Step 4. Prepare your data
If you haven’t already, stage your data in Coleman.
https://youtu.be/M_hPQa_GcRU?si=qDXRAGZUhaqRfo7f
Expand the datasets panel on the left side of the jupyterhub interface. Type the name of your loaded dataset and find it in the list. Select Load to see it appear in the list of loaded datasets.
Once you have loaded a dataset, a new folder named “datasets” will appear in the jupyterhub directory.
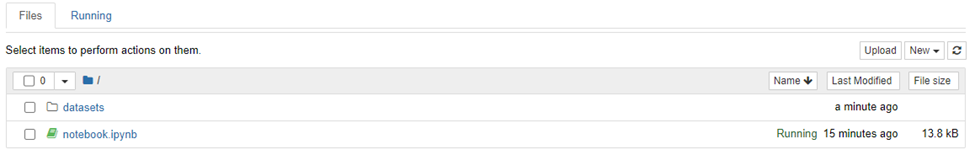
Use the folder structure to locate your dataset, and the subfolders it might live in, create an import command to bring your dataset into the kernel for use. Use a command like read_csv in pandas:
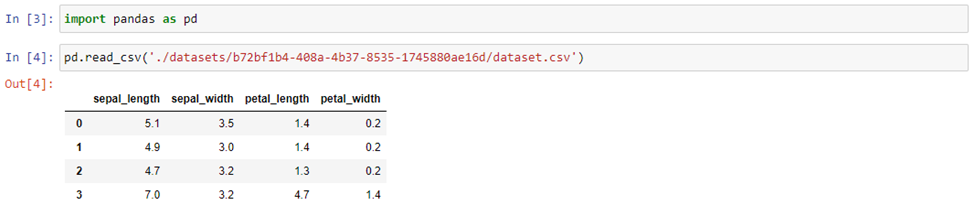
Step 5: Write your code!
Unleash your creative juices. Code, test, recode, and compare models. Shape your code into the train and predictor scripts and copy the appropriate code to their respective tabs.
Step 6. Import Hyperparameters:
Add your hyperparameters to the grid in the Hyperparameters tab and set their attributes (default values).
Step 7. Package and Deploy:
Package and deploy the custom algorithm using the Package Files and Deploy buttons at the top right of the custom algorithms interface.

Step 8: Use the algorithm in a quest
When building a quest, the custom algorithm activity block will now let you access the deployed package.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Implementing Custom Algorithms
Incremental ML Model Training
Overview
In Machine Learning, initial model training usually requires large data sets to train on to ensure reliable predictive models. Training is naturally intense on resource consumption and can be very time-consuming. In addition, a model's life cycle does not conclude with its initial creation -- it must be regularly retrained with the latest data to stay accurate and responsive to evolving environments. Incremental training allows users to efficiently update existing machine learning models with new data, enhancing performance without retraining from scratch -- significantly reducing computational resources and time required to retrain.
Components
- Machine Learning: Infor AI * Data Fabric: Data Lake
Requirements
- Infor AI Security Roles: * COLEMANAI-User * COLEMANAI-Administrator * A working Infor AI quest using a custom algorithm
Tutorial
Difficulty: Easy Estimated Completion Time: 10 minutes
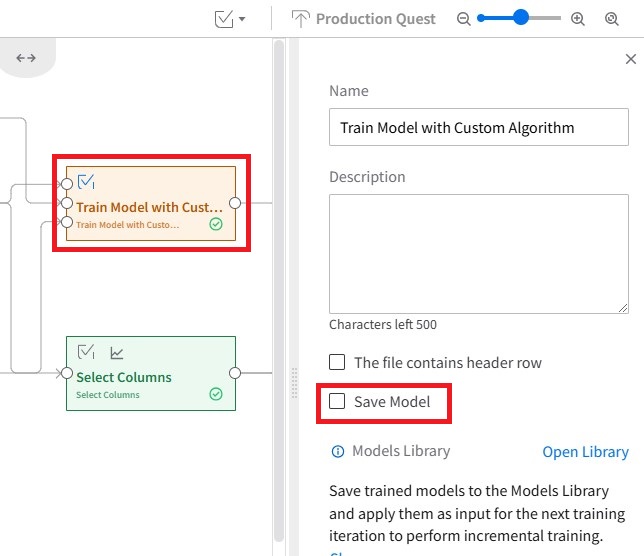
1. Save a custom algorithm
A saved custom algorithm is a requirement for incremental training. In an already existing quest, go to the "Train Model with Custom Algorithm" block, and make sure you have checked "Save Model." Once the quest has been executed, it will be stored in the Models Library.
2. Create the incremental dataset
Create a dataset in the Data Collection > Datasets section of the platform containing only the new and incremental data. For this activity, you are likely creating a new dataset from the data lake.
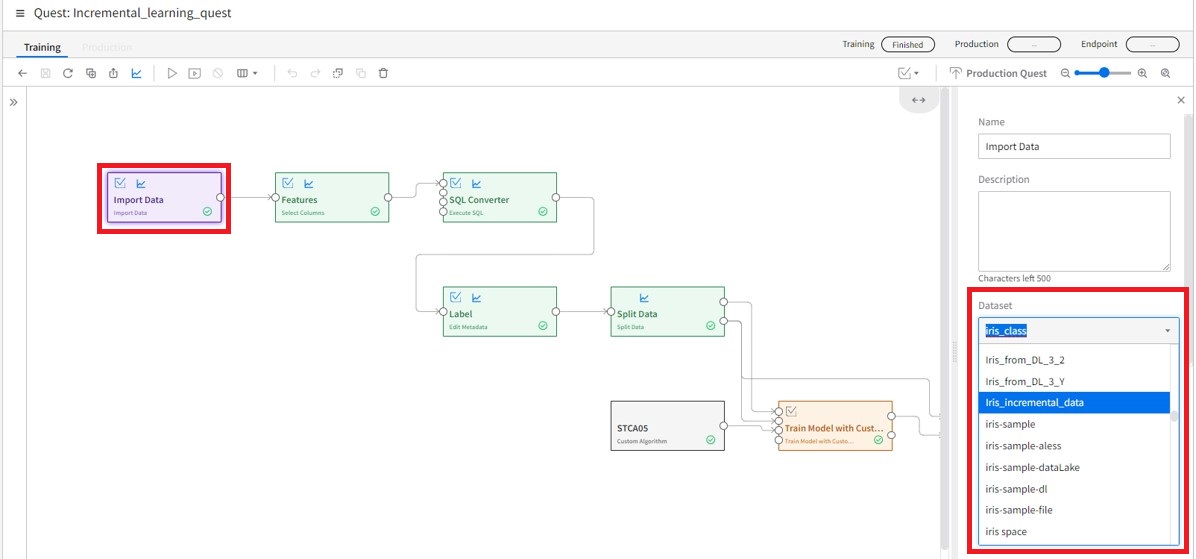
3. Update your quest data source
Go back to your quest and change the source of the data to the new set of incremental data.
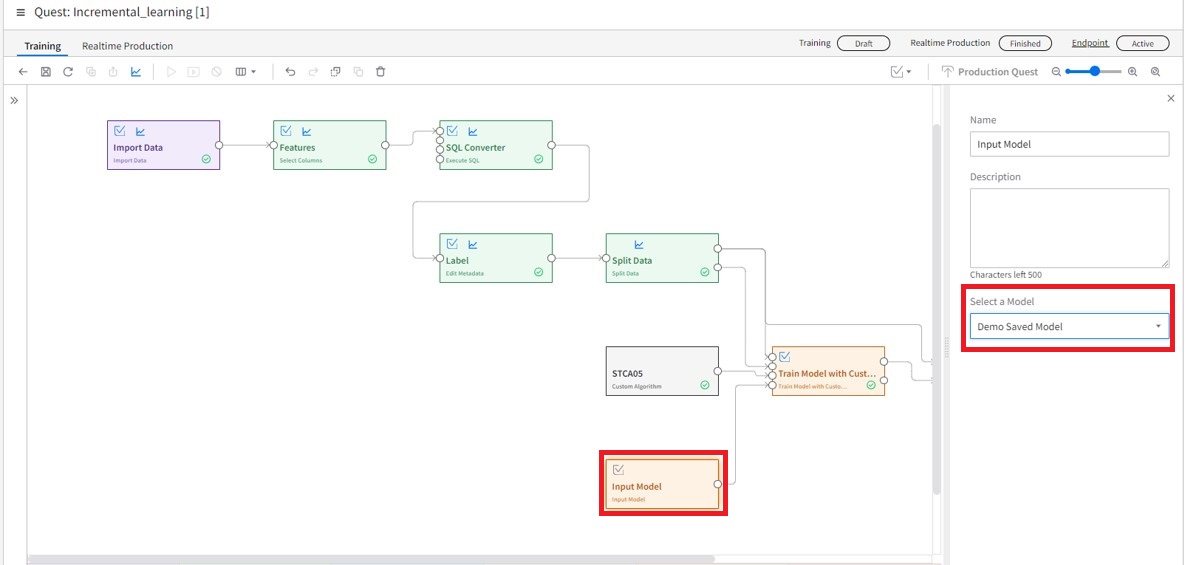
4. Use the Input Model activity
Add an Input Model block to the Quest. In the sidebar, select the saved model to be used, and feed the activity into the train custom algorithm block.
5. Update the saved model (or don't)
You may or may not want to save the new model after the retraining. Return to the "Train Model with Custom Algorithm" block and verify the "Save Model" box is checked if you'd like the new model saved or not checked if you do not wish to save new versions of the model.
6. Run the training quest
Save and run the quest. Once the execution is finished, your machine-learning model will be updated to include the new data!
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Incremental ML Model Training
Optimizing Assortment Selection
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Optimizing Assortment Selection
Using ad-hoc datasets
Overview
While most of your machine learning applications consume data from the data lake, you encountered a scenario where you need an ad-hoc import of a CSV file for some supplemental data for your machine learning model. While best practices suggest an automated import of periodic/updated data into the data lake, this is a time when a one-time-use dataset or a static dataset is required.
Components
Requirements
- Access to an Infor CloudSuite * User privileges to Infor AI * Delimited data on a local machine * Optional InforU courses: * Infor OS: Foundation for Multi-Tenant - Part 1 * Infor OS: Foundation for Multi-Tenant - Part 2 * Coleman AI Platform: Enablement Overview
Tutorial
Difficulty: Easy Estimated completion time: 5 Minutes
The datasets section of Infor AI is the staging area of data for machine learning consumption. Importing files is straightforward, with a few items of note to pay attention to.
1. Verify data structure
Blindly importing data is dangerous. It is good practice to understand your data before import. Know its structure, and its data types. Some attention to this on the front end will save effort on the development side. For import into Infor AI, your data must be in some delimited form, usually CSV. Tab separated data can also be read, or a custom delimiter can be used. Understanding which variables (columns) are numeric and which are strings is an important distinction as well. Infor AI will make some assumptions on datatypes, but in the end, you are the keeper of the data and should verify datatypes.
Additionally, pay attention to any special datatypes like date formats and time formats. These formats are often read in as strings and it takes some processing to treat them as date/time data.
Select the appropriate delimiter before data input. You will also have the opportunity to define any custom data formats. These are particularly important for data and time data as there are many accepted formats for such data. Identifying the format early will help process the data later. While certainly not an exhaustive list, common datetime formats can be found here for reference.
Your data should also be structured such that each variable is a column and each observation (or case) is a row. Your data may optionally have a header which gives names to each variable.
It is also best practice to have done some data investigation at this point. Understanding the extent of missing values, value distribution, and correlations in your data will help develop better machine learning models.
2. Import data
In the datasets section of Infor AI, click "+Add" and select import from "File". Use the navigator to find your file. Select the appropriate delimiter and identify any custom data type formats. You will also need to select if your file has a header or not.

3. Examine Metadata
Press the preview button after selecting your data file. This should give you a brief glimpse of the data below, as well as opening up the Metadata tab. Select Metadata and view your data types. Infor AI has made some guesses as to your data types (double/string/float/boolean etc.), and you can change any you need to customize. This is also where you can rename variables as desired-- particularly if your data did not have a header. You can always modify data types in a quest, but there are time savings and computational savings involved with setting these correctly on import.
4. Save and Examine
When happy with your metadata, click the save icon and Infor AI will process and load the data. Once complete, the Statistics tab will be available allowing you some insights into the structure of your data. This is a great place to double check for missing values, and to understand the spread and shape of your data.
5. Use your data
Your dataset is now ready for use in a quest. Import data blocks in any quest will now have your new data set available in the dropdown.
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Using ad-hoc datasets
Using API’s to access exposed Endpoints
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Using API’s to access exposed Endpoints
Best practices
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Best practices
Analytics & Reporting in CloudSuite Service Industries
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Analytics & Reporting in CloudSuite Service Industries
Analytics & Reporting in M3 Cloudsuites
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Analytics & Reporting in M3 Cloudsuites
Backend as a Service (BaaS)
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Data Fabric
Manage data on the platform so that humans and systems can securely access information from anywhere.
On this page
- Data Fabric
Digital Assistant
Streamline the user experience with a digital assistant that helps your employees navigate and access information by voice or chat.
On this page
- Digital Assistant
Document Management
Leverage Infor's central document repository to manage your enterprise document in the cloud.
On this page
- Document Management
Governance, Risk and Compliance
What made this section unhelpful for you?
On this page
- Governance, Risk and Compliance
Integration with ION
Create a unified application topology using the integration hub in the Infor Platform.
On this page
- Integration with ION
Portal and Workspaces
On this page
- Portal and Workspaces
Robotic Process Automation
RPA automates repetitive tasks and empowers your team to focus on what they do best.
On this page
- Robotic Process Automation
Security & User Management
Tutorials that help you leverage Infor's cloud security and user management capabilities.
On this page
- Security & User Management